The diagnosis and management of shoulder pain
- PMID: 30451406
- PMCID: PMC6442215
- DOI: 10.15557/JoU.2018.0034
The diagnosis and management of shoulder pain
Abstract
Diagnosis is crucial in decision-making when treating a patient with shoulder pain. Ultrasound is also very important in the diagnostic and therapeutic pathway, especially when surgery is being considered. This article outlines the diagnostic pathway using the patient's history, physical examination and ultrasound examination. It is important to correlate the clinical assessment with the imaging signs. It is also important to treat the patient and not the images as there may be abnormalities detected on imaging that are not symptomatic. The article covers the important diagnosis of subdeltoid subacromial bursitis, glenohumeral joint capsulitis, calcific tendinosis, acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis and long head of biceps tendinosis. It will guide the reader in how to use the findings to treat, using ultrasound-guided injection and other techniques, including steroid injections, hydrodilatation, barbotage and extracorporeal shockwave treatment. These are discussed with the knowledge from over 30 years of experience with a literature review evidential support. I have included tips to make these procedures more effective in treatment and final outcome. There is discussion regarding the use of steroid injections in the presence of a rotator cuff tear and how to proceed if the patient has more than one disease process. The sensible use of steroids and local anesthetics are included, bearing in mind that lidocaine and high concentrations of long-acting local anesthetics are chondrotoxic and should not be injected into joints.
Keywords: diagnosis; shoulder pain; treatment; ultrasound.
© Polish Ultrasound Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author does not report any financial or personal connections with other persons or organizations, which might negatively affect the contents of this publication and/or claim authorship rights to this publication.
Figures

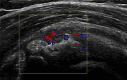
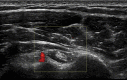
References
-
- Kelly SM, Brittle N, Allen GM: The value of physical tests for subacromial impingement syndrome: a study of diagnostic accuracy. Clin Rehabil 2010; 24: 149–58. - PubMed
-
- Kreuz PC, Steinwachs M, Angele P: Single-dose local anesthetics exhibit a type-, dose-, and time-dependent chondrotoxic effect on chondrocytes and cartilage: a systematic review of the current literature. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2018; 26: 819–830. - PubMed
-
- McMahon SE, LeRoux JA, Smith TO, Hing CB: Total joint arthroplasty following intra-articular steroid injection: a literature review. Acta Orthop Belg 2013; 79: 672–679. - PubMed
-
- Dean BJ, Franklin SL, Murphy RJ, Javaid MK, Carr AJ: Glucocorticoids induce specific ion-channel-mediated toxicity in human rotator cuff tendon: a mechanism underpinning the ultimately deleterious effect of steroid injection in tendinopathy? Br J Sports Med 2014; 48: 1620–1626. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
