Dosimetry for the study of medical radiation workers with a focus on the mean absorbed dose to the lung, brain and other organs
- PMID: 30451566
- PMCID: PMC9465996
- DOI: 10.1080/09553002.2018.1549756
Dosimetry for the study of medical radiation workers with a focus on the mean absorbed dose to the lung, brain and other organs
Abstract
Background: The reconstruction of lifetime radiation doses for medical workers presents special challenges not commonly encountered for the other worker cohorts comprising the Million Worker Study.
Methods: The selection of approximately 175,000 medical radiation workers relies on using estimates of lifetime and annual personal monitoring results collected since 1977. Approaches have been created to adjust the monitoring results so that mean organ absorbed doses can be estimated.
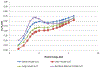
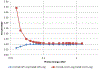
Results: Changes in medical technology and practices have altered the radiation exposure environments to which a worker may have been exposed during their career. Other temporal factors include shifts in regulatory requirements that influenced the conduct of radiation monitoring and the changes in the measured dose quantities.
Conclusions: The use of leaded aprons during exposure to lower energy X rays encountered in fluoroscopically based radiology adds complexity to account for the shielding of the organs located in the torso when dosimeters were worn over leaded aprons. Estimating doses to unshielded tissues such as the brain and lens of the eye become less challenging when dosimeters are worn at the collar above the apron. The absence of leaded aprons in the higher energy photon settings lead to a more straightforward process of relating dosimeter results to mean organ doses.
Keywords: Dosimetry; epidemiology; personal monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
The author’s report no conflicts of interest. RCY was employed by Landauer Inc. who provided the database being used by the NCRP for the Million Person Study. CNP is currently employed by Landauer, Inc. The work in preparing this paper is entirely voluntary, entails no financial implications and only involves the scientific interpretation and application of the radiation measurement data acquired many years ago by Landauer.
Figures


References
-
- [ANSI] American National Standards Institute. 1983. American National Standard for dosimetry – personnel dosimetry performance – criteria for testing. ANSI N13.11-1983. New York: American National Standards Institute.
-
- [ANSI] American National Standards Institute. 2001. American National Standard for dosimetry – personnel dosimetry performance – criteria for testing. ANSI N13.11-2001. New York: American National Standards Institute.
-
- Boice JD Jr. 2017. Space: the final frontier-research relevant to Mars. Health Phys. 112:392–397. - PubMed
-
- Boice JD Jr. 2019. Relevance of the Million Person Study to research needs for NASA and space exploration. Int J Radiat Biol. Submitted. - PubMed
-
- Boice JD Jr, Ellis ED, Golden AP, Girardi DJ, Cohen SS, Chen H, Mumma MT, Shore RE, Leggett RW. 2018. The past informs the future: an overview of the Million Worker Study and The Mallinckrodt Chemical Works Cohort. Health Phys. 114:381–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
