Age-related declines in α-Klotho drive progenitor cell mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired muscle regeneration
- PMID: 30451844
- PMCID: PMC6242898
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07253-3
Age-related declines in α-Klotho drive progenitor cell mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired muscle regeneration
Abstract
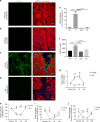
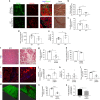
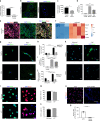
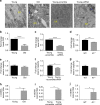
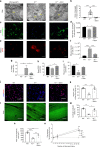
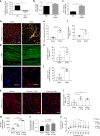
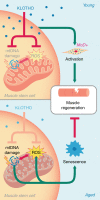
While young muscle is capable of restoring the original architecture of damaged myofibers, aged muscle displays a markedly reduced regeneration. We show that expression of the "anti-aging" protein, α-Klotho, is up-regulated within young injured muscle as a result of transient Klotho promoter demethylation. However, epigenetic control of the Klotho promoter is lost with aging. Genetic inhibition of α-Klotho in vivo disrupted muscle progenitor cell (MPC) lineage progression and impaired myofiber regeneration, revealing a critical role for α-Klotho in the regenerative cascade. Genetic silencing of Klotho in young MPCs drove mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage and decreased cellular bioenergetics. Conversely, supplementation with α-Klotho restored mtDNA integrity and bioenergetics of aged MPCs to youthful levels in vitro and enhanced functional regeneration of aged muscle in vivo in a temporally-dependent manner. These studies identify a role for α-Klotho in the regulation of MPC mitochondrial function and implicate α-Klotho declines as a driver of impaired muscle regeneration with age.
Conflict of interest statement
M.F. is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Company. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Schultz E. Satellite cell behavior during skeletal muscle growth and regeneration. Med. & Sci. Sports & Exerc. 1989;21(5 Suppl):S181–S186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

