Intracellular emetic signaling cascades by which the selective neurokinin type 1 receptor (NK1R) agonist GR73632 evokes vomiting in the least shrew (Cryptotis parva)
- PMID: 30453005
- PMCID: PMC6294657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.11.012
Intracellular emetic signaling cascades by which the selective neurokinin type 1 receptor (NK1R) agonist GR73632 evokes vomiting in the least shrew (Cryptotis parva)
Abstract
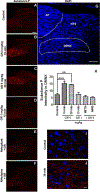
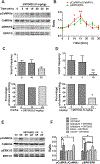
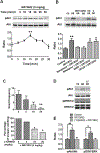
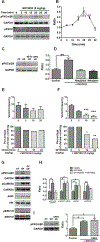
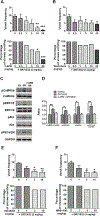
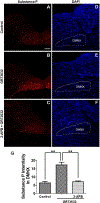
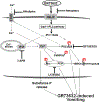
To characterize mechanisms involved in neurokinin type 1 receptor (NK1R)-mediated emesis, we investigated the brainstem emetic signaling pathways following treating least shrews with the selective NK1R agonist GR73632. In addition to episodes of vomiting over a 30-min observation period, a significant increase in substance P-immunoreactivity in the emetic brainstem dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMNX) occurred at 15 min post an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection GR73632 (5 mg/kg). In addition, time-dependent upregulation of phosphorylation of several emesis -associated protein kinases occurred in the brainstem. In fact, Western blots demonstrated significant phosphorylations of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase IIα (CaMKIIα), extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase1/2 (ERK1/2), protein kinase B (Akt) as well as α and βII isoforms of protein kinase C (PKCα/βII). Moreover, enhanced phospho-ERK1/2 immunoreactivity was also observed in both brainstem slices containing the dorsal vagal complex emetic nuclei as well as in jejunal sections from the shrew small intestine. Furthermore, our behavioral findings demonstrated that the following agents suppressed vomiting evoked by GR73632 in a dose-dependent manner: i) the NK1R antagonist netupitant (i.p.); ii) the L-type Ca2+ channel (LTCC) antagonist nifedipine (subcutaneous, s.c.); iii) the inositol trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) antagonist 2-APB (i.p.); iv) store-operated Ca2+ entry inhibitors YM-58483 and MRS-1845, (i.p.); v) the ERK1/2 pathway inhibitor U0126 (i.p.); vi) the PKC inhibitor GF109203X (i.p.); and vii) the inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway LY294002 (i.p.). Moreover, NK1R, LTCC, and IP3R are required for GR73632-evoked CaMKIIα, ERK1/2, Akt and PKCα/βII phosphorylation. In addition, evoked ERK1/2 phosphorylation was sensitive to inhibitors of PKC and PI3K. These findings indicate that the LTCC/IP3R-dependent PI3K/PKCα/βII-ERK1/2 signaling pathways are involved in NK1R-mediated vomiting.
Keywords: Brainstem; ERK1/2; Emesis; GR73632; Gut; NK(1) receptor.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
We have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
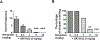
References
-
- Amadoro G, Pieri M, Ciotti MT, Carunchio I, Canu N, Calissano P, Zona C, Severini C. Substance P provides neuroprotection in cerebellar granule cells through Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 activation: evidence for the involvement of the delayed rectifier potassium current. Neuropharmacology 2007; 52: 1366–1377. - PubMed
-
- Andrews PLR, Rudd JA. The role of tachykinins and the tachykinin NK1 receptor in nausea and emesis. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2004; 164: 359–440.
-
- Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, Yeol Kim J, Abraham E. Involvement of PKCalpha/beta in TLR4 and TLR2 dependent activation of NF-kappaB. Cell Signal 2005; 17: 385–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

