Localization of the kinase Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated to Adenovirus E4 mutant DNA replication centers is important for its inhibitory effect on viral DNA accumulation
- PMID: 30453211
- PMCID: PMC6874311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.11.003
Localization of the kinase Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated to Adenovirus E4 mutant DNA replication centers is important for its inhibitory effect on viral DNA accumulation
Abstract
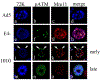
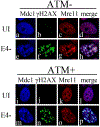
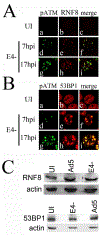
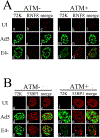
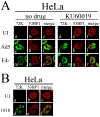
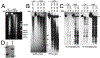
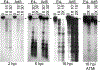
Adenovirus (Ad) type 5 (Ad5) E4 deletion mutants including H5dl1007 (E4-) induce a DNA damage response (DDR) that activates the kinase ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM), which can interfere with efficient viral DNA replication. We find that localization of active phosphorylated ATM (pATM) to E4- viral replication centers (VRCs) is important for its inhibitory effect. ATM is necessary for localization of RNF8 and 53BP1 to E4 mutant VRCs, while recruitment of DDR factors Mre11, Mdc1 and γH2AX is ATM-independent, raising the possibility that ATM may affect viral chromatin at VRCs. We assessed E4- and Ad5 chromatin organization by micrococcal nuclease (MN) digestion. A significant fraction of Ad5 DNA is somewhat resistant to MN digestion, whereas E4- DNA is more susceptible. ATM inhibition increases the fraction of E4- DNA that is resistant to MN digestion. Our results address possible mechanisms through which ATM inhibits E4- DNA replication.
Keywords: 53BP1; ATM; Adenovirus; DNA damage response; E4 11 kDa; E4 34 kDa; E4 ORF 3; E4 ORF 6; Micrococcal nuclease; RNF8.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB, 2003. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421 (6922), 499–506. - PubMed
-
- Bekker-Jensen S, Mailand N, 2010. Assembly and function of DNA double-strand break repair foci in mammalian cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 9 (12), 1219–1228. - PubMed
-
- Blackford AN, Jackson SP, 2017. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: The Trinity at the Heart of the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cell 66 (6), 801–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

