Site-Specific N-Glycosylation on the AAV8 Capsid Protein
- PMID: 30453606
- PMCID: PMC6266768
- DOI: 10.3390/v10110644
Site-Specific N-Glycosylation on the AAV8 Capsid Protein
Abstract
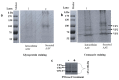
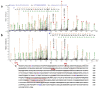
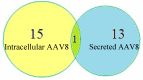
Adeno associated virus (AAV) is a versatile gene delivery tool, which has been approved as a human gene therapy vector for combating genetic diseases. AAV capsid proteins are the major components that determine the tissue specificity, immunogenicity and in vivo transduction performance of the vector. In this study, the AAV8 capsid glycosylation profile was systemically analyzed by peptide mass fingerprinting utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometry to determine the presence of capsid glycosylation. We identified N-glycosylation on the amino acid N499 of the capsid protein. We characterized the overall sugar profile for vector produced in 293 cells. Multiple N-glycosylated host-cell proteins (HCPs) copurified with AAV8 vectors and were identified by analyzing LC-MS data utilizing a human database and proteome discoverer search engine. The N-glycosylation analysis by MALDI-TOF MS, highlighted the probability of AAV8 interaction with terminal galactosylated N-glycans within the HCPs.
Keywords: Adeno associated virus; host cell protein analysis; mass spectrometry; site specific N-glycan analysis; virus-host interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vance M.A., Mitchell A., Samulski R.J. AAV Biology, Infectivity and Therapeutic Use from Bench to Clinic. Gene Ther. Princ. Chall. 2015 doi: 10.5772/61988. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

