High-Dose Rifamycins Enable Shorter Oral Treatment in a Murine Model of Mycobacterium ulcerans Disease
- PMID: 30455239
- PMCID: PMC6355596
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01478-18
High-Dose Rifamycins Enable Shorter Oral Treatment in a Murine Model of Mycobacterium ulcerans Disease
Abstract
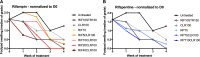
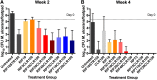
Buruli ulcer (BU), caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans, is a neglected tropical skin and soft tissue infection that is associated with disability and social stigma. The mainstay of BU treatment is an 8-week course of rifampin (RIF) at 10 mg/kg of body weight and 150 mg/kg streptomycin (STR). Recently, the injectable STR has been shown to be replaceable with oral clarithromycin (CLR) for smaller lesions for the last 4 weeks of treatment. A shorter, all-oral, highly efficient regimen for BU is needed, as the long treatment duration and indirect costs currently burden patients and health systems. Increasing the dose of RIF or replacing it with the more potent rifamycin drug rifapentine (RPT) could provide such a regimen. Here, we performed a dose-ranging experiment of RIF and RPT in combination with CLR over 4 weeks of treatment in a mouse model of M. ulcerans disease. A clear dose-dependent effect of RIF on both clinical and microbiological outcomes was found, with no ceiling effect observed with tested doses up to 40 mg/kg. RPT-containing regimens were more effective on M. ulcerans All RPT-containing regimens achieved culture negativity after only 4 weeks, while only the regimen with the highest RIF dose (40 mg/kg) did so. We conclude that there is dose-dependent efficacy of both RIF and RPT and that a ceiling effect is not reached with the current standard regimen used in the clinic. A regimen based on higher rifamycin doses than are currently being evaluated against tuberculosis in clinical trials could shorten and improve therapy of Buruli ulcer.
Keywords: Buruli ulcer; Mycobacterium ulcerans; clarithromycin; high-dose rifamycins; rifampin; rifapentine.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
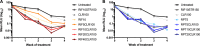
References
-
- de Zeeuw J, Omansen TF, Douwstra M, Barogui YT, Agossadou C, Sopoh GE, Phillips RO, Johnson C, Abass KM, Saunderson P, Dijkstra PU, van der Werf TS, Stienstra Y, Stientstra Y. 2014. Persisting social participation restrictions among former Buruli ulcer patients in Ghana and Benin. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8:e3303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. 2018. Buruli ulcer (Mycobacterium ulcerans infection). WHO, Geneva, Switzerland: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/buruli-ulcer-(mycobacter.... Accessed 1 November 2018.
-
- Etuaful S, Carbonnelle B, Grosset J, Lucas S, Horsfield C, Phillips R, Evans M, Ofori-Adjei D, Klustse E, Owusu-Boateng J, Amedofu GK, Awuah P, Ampadu E, Amofah G, Asiedu K, Wansbrough-Jones M. 2005. Efficacy of the combination rifampin-streptomycin in preventing growth of Mycobacterium ulcerans in early lesions of Buruli ulcer in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:3182–3186. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3182-3186.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

