A LysM Domain Intervenes in Sequential Protein-Protein and Protein-Peptidoglycan Interactions Important for Spore Coat Assembly in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 30455281
- PMCID: PMC6351740
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00642-18
A LysM Domain Intervenes in Sequential Protein-Protein and Protein-Peptidoglycan Interactions Important for Spore Coat Assembly in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
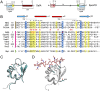
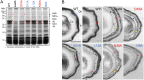
At a late stage in spore development in Bacillus subtilis, the mother cell directs synthesis of a layer of peptidoglycan known as the cortex between the two forespore membranes, as well as the assembly of a protective protein coat at the surface of the forespore outer membrane. SafA, the key determinant of inner coat assembly, is first recruited to the surface of the developing spore and then encases the spore under the control of the morphogenetic protein SpoVID. SafA has a LysM peptidoglycan-binding domain, SafALysM, and localizes to the cortex-coat interface in mature spores. SafALysM is followed by a region, A, required for an interaction with SpoVID and encasement. We now show that residues D10 and N30 in SafALysM, while involved in the interaction with peptidoglycan, are also required for the interaction with SpoVID and encasement. We further show that single alanine substitutions on residues S11, L12, and I39 of SafALysM that strongly impair binding to purified cortex peptidoglycan affect a later stage in the localization of SafA that is also dependent on the activity of SpoVE, a transglycosylase required for cortex formation. The assembly of SafA thus involves sequential protein-protein and protein-peptidoglycan interactions, mediated by the LysM domain, which are required first for encasement then for the final localization of the protein in mature spores.IMPORTANCEBacillus subtilis spores are encased in a multiprotein coat that surrounds an underlying peptidoglycan layer, the cortex. How the connection between the two layers is enforced is not well established. Here, we elucidate the role of the peptidoglycan-binding LysM domain, present in two proteins, SafA and SpoVID, that govern the localization of additional proteins to the coat. We found that SafALysM is a protein-protein interaction module during the early stages of coat assembly and a cortex-binding module at late stages in morphogenesis, with the cortex-binding function promoting a tight connection between the cortex and the coat. In contrast, SpoVIDLysM functions only as a protein-protein interaction domain that targets SpoVID to the spore surface at the onset of coat assembly.
Keywords: LysM domain; SpoVID; peptidoglycan-binding protein; spore coat; spore cortex; sporulation.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interaction between coat morphogenetic proteins SafA and SpoVID.J Bacteriol. 2006 Nov;188(22):7731-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.00761-06. Epub 2006 Sep 1. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16950916 Free PMC article.
-
SpoVID guides SafA to the spore coat in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2001 May;183(10):3041-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.10.3041-3049.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11325931 Free PMC article.
-
SpoVID functions as a non-competitive hub that connects the modules for assembly of the inner and outer spore coat layers in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 2018 Nov;110(4):576-595. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14116. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Mol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30168214 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification and characterization of the outermost layer of Bacillus subtilis spores].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012;132(8):919-24. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.132.919. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 22864350 Review. Japanese.
-
Assembly and genetics of spore protective structures.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002 Mar;59(3):434-44. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8436-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 11964122 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toad's survivability and soil microbiome alterations impacted via individual abundance.Biol Futur. 2025 Sep;76(3):399-411. doi: 10.1007/s42977-025-00261-7. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Biol Futur. 2025. PMID: 40478395
-
Bacterial developmental checkpoint that directly monitors cell surface morphogenesis.Dev Cell. 2022 Feb 7;57(3):344-360.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.12.021. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Dev Cell. 2022. PMID: 35065768 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Novel Regulator of Clostridioides difficile Cortex Formation.mSphere. 2021 Jun 30;6(3):e0021121. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00211-21. Epub 2021 May 28. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34047655 Free PMC article.
-
RagB stimulates the activity of the peptidoglycan polymerase RodA in Bacillus subtilis.EMBO Rep. 2025 Aug 15. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00547-w. Online ahead of print. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 40817173
-
DNA damage checkpoint activation affects peptidoglycan synthesis and late divisome components in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 2021 Aug;116(2):707-722. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14765. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34097787 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

