Discovery of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus-encoded circular RNAs and a human antiviral circular RNA
- PMID: 30455306
- PMCID: PMC6294913
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1816183115
Discovery of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus-encoded circular RNAs and a human antiviral circular RNA
Abstract
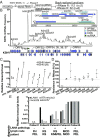
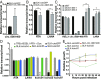
Noncoding RNAs have substantial effects in host-virus interactions. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are novel single-stranded noncoding RNAs which can decoy other RNAs or RNA-binding proteins to inhibit their functions. The role of circRNAs is largely unknown in the context of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV). We hypothesized that circRNAs influence viral infection by inhibiting host and/or viral factors. Transcriptome analysis of KSHV-infected primary endothelial cells and a B cell line identified human circRNAs that are differentially regulated upon infection. We confirmed the expression changes with divergent PCR primers and RNase R treatment of specific circRNAs. Ectopic expression of hsa_circ_0001400, a circRNA induced by infection, suppressed expression of key viral latent gene LANA and lytic gene RTA in KSHV de novo infections. Since human herpesviruses express noncoding RNAs like microRNAs, we searched for viral circRNAs encoded in the KSHV genome. We performed circRNA-Seq analysis with RNase R-treated, circRNA-enriched RNA from KSHV-infected cells. We identified multiple circRNAs encoded by the KSHV genome that are expressed in KSHV-infected endothelial cells and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cells. The KSHV circRNAs are located within ORFs of viral lytic genes, are up-regulated upon the induction of the lytic cycle, and alter cell growth. Viral circRNAs were also detected in lymph nodes from patients of KSHV-driven diseases such as PEL, Kaposi's sarcoma, and multicentric Castleman's disease. We revealed new host-virus interactions of circRNAs: human antiviral circRNAs are activated in response to KSHV infection, and viral circRNA expression is induced in the lytic phase of infection.
Keywords: KSHV; circRNA-Seq; circular RNA; herpesvirus; noncoding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: T.S.U. is a coinventor on a patent application related to the treatment of KSHV-associated diseases with pomalidomide. This invention was made as part of his duties as an employee of the US government, and the patents are or will be assigned to the US Department of Health and Human Services. The government may convey a portion of the royalties it receives from licensure of its patents to its employee inventors. T.S.U. has recently conducted clinical research using drugs supplied to the National Cancer Institute through cooperative research and development agreements with Celgene Corp., Merck and Co., and Hoffman LaRoche.
Figures

Comment in
-
'RNA circles of influence' in Kaposi sarcoma.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Jul;7(Suppl 3):S109. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.05.17. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31576316 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded circRNAs Are Expressed in Infected Tumor Tissues and Are Incorporated into Virions.mBio. 2020 Jan 7;11(1):e03027-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03027-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 31911496 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Gammaherpesvirus Circular RNA Repertoires: Conserved and Unique Viral Circular RNAs.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e01952-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01952-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30567979 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Nrf2 Interacts with Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency Protein LANA-1 and Host Protein KAP1 To Mediate Global Lytic Gene Repression.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7874-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00895-15. Epub 2015 May 20. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25995248 Free PMC article.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
-
miRNAs and their roles in KSHV pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2019 Jun;266:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.03.024. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Virus Res. 2019. PMID: 30951791 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of circRNAs in Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Associated Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1173. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051173. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction and Bioinformatics Analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network in Acute Myocardial Infarction.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 29;13:854993. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.854993. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35422846 Free PMC article.
-
LIMD2 is the Signature of Cell Aging-immune/Inflammation in Acute Myocardial Infarction.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(17):2400-2413. doi: 10.2174/0109298673274563231031044134. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37936458
-
Biogenesis and Functions of Circular RNAs Come into Focus.Trends Cell Biol. 2020 Mar;30(3):226-240. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2019.12.004. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Trends Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31973951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Modifications and Their Role in Regulating KSHV Replication and Pathogenic Mechanisms.J Med Virol. 2025 Jan;97(1):e70140. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70140. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 39740054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

