Clinical Utility of Intravenous Nifekalant Injection during Radiofrequency catheter Ablation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 30455835
- PMCID: PMC6207242
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.1839
Clinical Utility of Intravenous Nifekalant Injection during Radiofrequency catheter Ablation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) for persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) is still challenging even in RFCA-era for AF. The aim of this study was to assess the clinical utility of nifekalant, a pure potassium channel blocker,during RFCA for persistent AF.
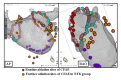
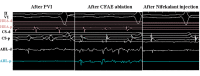
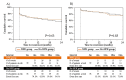
Methods and results: We retrospectively enrolled 157 consecutive persistentAF patientsundergoing first RFCA procedure withcomplex fractionated atrial electrogram (CFAE)ablation after pulmonary veins isolation and compared outcomes between patientswith (NFK group: N=79) and without (No-NFK group: N=78)additional CFAE ablation using intravenous nifekalant (0.3mg/kg). Primary endpoint was 24-month atrial arrhythmia-free survival post ablation.The prevalence of AF terminationwas significantly higher in NFK group than No-NFK group (64.6% versus 7.7%, P<0.001). Arrhythmia-free survival, however, was not significantly different between 2 groups (61.5% versus 54.1%, P=0.63).There was no significant difference between 2 groups in the prevalence of recurrent atrial tachycardia(25.0% versus 23.5%, P=0.89). Arrhythmia-free survivalin patients with AF termination during procedure was significantly higher thanthose without (73.0% versus 41.0%, P=0.002; adjusted hazard ratio 0.48, 95% confidence interval 0.17-0.84, P=0.02) amongNFK group,but not amongNo-NFK group (66.7% versus 53.2%, P=0.53).
Conclusions: Intravenous nifekalant injection during additional CFAE ablation did not improve sinus maintenancerate after RFCA procedure for AF, but AF termination by nifekalant injection could be a clinical predictor of better success rates after procedure.
Keywords: Complex Fractionated Atrial Electrogram; Nifekalant; Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation; Spersistentatrial Fibrillation.
Figures



References
-
- Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah D C, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Métayer P, Clémenty J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998 Sep 03;339 (10):659–66. - PubMed
-
- Pappone Carlo, Augello Giuseppe, Sala Simone, Gugliotta Filippo, Vicedomini Gabriele, Gulletta Simone, Paglino Gabriele, Mazzone Patrizio, Sora Nicoleta, Greiss Isabelle, Santagostino Andreina, LiVolsi Laura, Pappone Nicola, Radinovic Andrea, Manguso Francesco, Santinelli Vincenzo. A randomized trial of circumferential pulmonary vein ablation versus antiarrhythmic drug therapy in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the APAF Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006 Dec 05;48 (11):2340–7. - PubMed
-
- Piccini Jonathan P, Lopes Renato D, Kong Melissa H, Hasselblad Vic, Jackson Kevin, Al-Khatib Sana M. Pulmonary vein isolation for the maintenance of sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009 Dec;2 (6):626–33. - PubMed
-
- January Craig T, Wann L Samuel, Alpert Joseph S, Calkins Hugh, Cigarroa Joaquin E, Cleveland Joseph C, Conti Jamie B, Ellinor Patrick T, Ezekowitz Michael D, Field Michael E, Murray Katherine T, Sacco Ralph L, Stevenson William G, Tchou Patrick J, Tracy Cynthia M, Yancy Clyde W. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014 Dec 02;130 (23):2071–104. - PubMed
-
- Camm A John, Lip Gregory Y H, De Caterina Raffaele, Savelieva Irene, Atar Dan, Hohnloser Stefan H, Hindricks Gerhard, Kirchhof Paulus. 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur. Heart J. 2012 Nov;33 (21):2719–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
