Molecular landscape and targeted therapy of acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 30455953
- PMCID: PMC6225571
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-018-0146-7
Molecular landscape and targeted therapy of acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
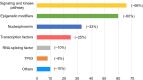
For decades, genetic aberrations including chromosome and molecular abnormalities are important diagnostic and prognostic factors in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). ATRA and imatinib have been successfully used in AML and chronic myelogenous leukemia, which proved that targeted therapy by identifying molecular lesions could improve leukemia outcomes. Recent advances in next generation sequencing have revealed molecular landscape of AML, presenting us with many molecular abnormalities. The individual prognostic information derived from a specific mutation could be modified by other molecular lesions. Therefore, the genomic complexity in AML poses a huge challenge to successful translation into more accurate risk stratification and targeted therapy. Herein, a summary of these mutations and targeted therapies are described. We focus on the prognostic information of recent identified molecular lesions and emerging targeted therapy.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia, Molecular landscape, Targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, Walker H, Chatters S, Goldstone AH, et al. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116:354–365. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-254441. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

