Alteration in thiols homeostasis, protein and lipid peroxidation in renal tissue following subacute oral exposure of imidacloprid and arsenic in Wistar rats
- PMID: 30456172
- PMCID: PMC6231080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.11.003
Alteration in thiols homeostasis, protein and lipid peroxidation in renal tissue following subacute oral exposure of imidacloprid and arsenic in Wistar rats
Abstract
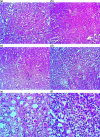
The aim of present study was to assess whether No Observed Effect Level (NOEL) of imidacloprid (IMI) potentiates the arsenic induced renal toxicity at its maximum contaminant level in drinking water in Wistar rats. Significant elevation of lipid and protein oxidation with reduced level of total thiols and antioxidant enzymes (catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione reductase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione-s-transferase) in renal tissue may have contributed to increased renal plasma biomarkers (creatinine and blood urea nitrogen) following repeated exposure of IMI and arsenic alone and in-combination. The altered renal biomarkers in co-exposed groups corroborated with histopathological alterations in renal tissue. The observations indicated that altered thiol homeostasis in renal tissue may be associated with increased lipid and protein oxidation in IMI and arsenic administered rats. It is concluded that administration of IMI potentiate the arsenic induced renal damage in Wistar rats.
Keywords: Arsenic; Imidacloprid; Malondialdehyde; Nephrotoxicity; Thiols.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maximum contaminant level of arsenic in drinking water potentiates quinalphos-induced renal damage on co-administration of both arsenic and quinalphos in Wistar rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jun;27(17):21331-21340. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08643-1. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32270456
-
Potentiating effect of imidacloprid on arsenic-induced testicular toxicity in Wistar rats.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Jul 31;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0239-9. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30064523 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic effects of imidacloprid combined with arsenic: Oxidative stress in rat liver.Toxicol Ind Health. 2018 Oct;34(10):726-735. doi: 10.1177/0748233718778993. Epub 2018 Jul 22. Toxicol Ind Health. 2018. PMID: 30033815
-
Repeated preexposure or coexposure to arsenic differentially alters acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress in rat kidney.Environ Toxicol. 2011 Jun;26(3):250-9. doi: 10.1002/tox.20551. Environ Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 19950220
-
Silibinin ameliorates arsenic induced nephrotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Dec;39(12):11201-16. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2029-6. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. Retraction in: Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jun;48(6):5377. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06475-x. PMID: 23070905 Retracted.
Cited by
-
Salivary Redox Homeostasis in Human Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 3;23(17):10076. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710076. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis as a mechanism of non-ferrous metal toxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Sep;96(9):2391-2417. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03317-y. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35727353 Review.
-
Fucoidan Modulated Oxidative Stress and Caspase-3 mRNA Expression Induced by Sulfoxaflor in the Brain of Mice.Neurotox Res. 2021 Dec;39(6):1908-1919. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00415-0. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 34570347
-
Gallic acid protects rat liver mitochondria ex vivo from bisphenol A induced oxidative stress mediated damages.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Jun 17;6:578-589. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.06.011. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31293903 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Quercetin and Ginger (Zingiber officinale) Extract against Dimethoate Potentiated Fluoride-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats.Foods. 2023 May 5;12(9):1899. doi: 10.3390/foods12091899. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37174437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levey A.S., Schoolwerth A.C., Burrows N.R. Comprehensive public health strategies for preventing the development, progression and complications of CKD: report of an expert panel convened by the Centres for Disease control and Prevention. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009;53:522–535. - PubMed
-
- Araujo M., Welch W.J. Oxidative stress and nitric oxide in kidney function. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2006;15(1):72–77. - PubMed
-
- Barsoum R.S. Chronic kidney disease in the developing world. New Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:997–999. - PubMed
-
- Uchino S. The epidemiology of acute renal failure in the world. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care. 2006;12:538–543. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

