Burden of Herpes Zoster in the Japanese Population with Immunocompromised/Chronic Disease Conditions: Results from a Cohort Study Claims Database from 2005-2014
- PMID: 30456446
- PMCID: PMC6380970
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-018-0268-8
Burden of Herpes Zoster in the Japanese Population with Immunocompromised/Chronic Disease Conditions: Results from a Cohort Study Claims Database from 2005-2014
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study is to describe the disease burden and costs of herpes zoster (HZ) in the general adult Japanese population or patients with immunocompromised (IC) conditions or chronic disorders.
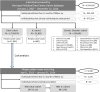
Methods: A retrospective cohort study of individuals aged 18-74 years was conducted using January 2005 to December 2014 records from the Japan Medical Data Center claims database. Twenty-eight IC conditions and chronic disorders were defined by diagnosis codes and/or procedures/treatments. HZ and its related complications were identified. Incidence rates (IR), frequency of HZ-related complications, healthcare resource utilization (HRU), and direct medical costs were estimated. HRU and costs were estimated on a subcohort of HZ cases occurring April 2012-January 2014.
Results: The overall IR of HZ in the total cohort of 2,778,476 adults was 4.92/1000 person-years (PY) [95% confidence interval (CI): 4.86-4.98] and increased with age. The IR in the IC cohort (51,818 subjects) was 8.87/1000 PY (95% CI: 8.29-9.48), ranging from 5.55/1000 PY (95% CI: 4.26-7.09) in psoriasis to 151.68/1000 PY (95% CI: 111.45-201.71) in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients; most IRs were in the range 6-10/1000 PY. The IRs in individuals with chronic disorders were also relatively high, in the range 5.40-12.90/1000 PY. The frequency of postherpetic neuralgia was 4.01% (95% CI: 3.72-4.33) in the total cohort and 11.73% (95% CI: 9.01-14.93) in the IC cohort. The mean [standard deviation (SD)] number of outpatient visits was 3.4 (4.9) and 5.0 (5.7), respectively, and the proportion of HZ patients hospitalized was 2.20% and 6.70%, respectively. The mean (SD) direct medical cost per HZ episode was ¥34,664 (¥54,433) and ¥55,201 (¥92,642) in the total and IC cohort, respectively.
Conclusions: The elevated burden of HZ in Japanese individuals harboring IC conditions and chronic disorders documented in our study underlines the need for prevention of HZ in people with these conditions.
Funding: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA.
Keywords: Claims database; Healthcare resource utilization; Herpes zoster; Immunocompromised; Japan; Medical cost; Postherpetic neuralgia.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

