Association between small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and toll-like receptor 4 in patients with pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 30457560
- PMCID: PMC6408165
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2018.17512
Association between small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and toll-like receptor 4 in patients with pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Background/aims: Multiple factors have been linked to pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer and cholangiocarcinoma. Until now, few studies have investigated the role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) signaling in these diseases. This study aimed to examine the relationship between the prevalence of SIBO and the TLR-4 expression in patients with pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma.
Materials and methods: A total of 90 human subjects suffering from pancreatic carcinoma (n=30), cholangiocarcinoma (n=30), and healthy controls (n=30) were enrolled in the study. A glucose hydrogen breath test (GHBT) was used to evaluate SIBO. The TLR4 protein expression was measured by immunohistochemistry (IHC).
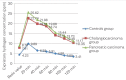
Results: The positive rate of SIBO was 63.3% in the pancreatic cancer group and 46.7% in patients with cholangiocarcinoma, which was significantly greater than 13.3% in the healthy control group (p<0.05). An IHC analysis revealed that the TLR-4 protein expression in the SIBO-positive pancreatic carcinoma patients was significantly higher than that in the SIBO-negative patients (p<0.05), and the same result was in the cholangiocarcinoma subjects. In addition, a correlation analysis identified the positive relationship between the prevalence of SIBO and the TLR-4 protein expression in pancreatic carcinoma (r=0.489), and the same result was in the cholangiocarcinoma subjects.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate a high prevalence of SIBO in pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma, and SIBO displays a positive correlation with the TLR-4 expression, suggesting that SIBO could be a risk factor for the pathogenesis of pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma, in which the TLR4 signaling may be involved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bustillo Ivan, Larson Heidi, Saif Muhammad Wasif. Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth: An Underdiagnosed Cause of Diarrhea in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. JOP. 2009;10:576–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
