Comorbidities in polymyalgia rheumatica: a systematic review
- PMID: 30458857
- PMCID: PMC6247740
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-018-1757-y
Comorbidities in polymyalgia rheumatica: a systematic review
Abstract
Background and aim: Comorbidities are known to exist in many rheumatological conditions. Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a common inflammatory rheumatological condition affecting older people which, prior to effective treatment, causes severe disability. Our understanding of associated comorbidities in PMR is based only on case reports or series and small cohort studies. The objective of this study is to review systematically the existing literature on the comorbidities associated with PMR.
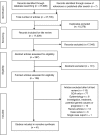
Methods: MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO and CINAHL databases were searched for original observational research from inception to November 2016. Papers containing the words 'Polymyalgia Rheumatica' OR 'Giant Cell Arteritis' OR the terms 'PMR' OR 'GCA' were included. Article titles were reviewed based on pre-defined criteria by two reviewers. Following selection for inclusion, studies were quality assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa tool and data were extracted.
Results: A total of 17,329 papers were reviewed and 41 were incorporated in this review, including three published after the search took place. Wide variations were found in study design, comorbidities reported and populations studied. Positive associations were found between PMR diagnosis and stroke, cardiovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, diverticular disease and hypothyroidism. Two studies reported a positive association between PMR and overall malignancy rate. Seven studies reported an association between PMR and specific types of cancer, such as leukaemia, lymphoma, myeloproliferative disease and specified solid tumours, although nine studies found either no or negative association between cancer and PMR.
Conclusion: Quantification of the prevalence of comorbidities in PMR is important to accurately plan service provision and enable identification of cases of PMR which may be more difficult to treat. This review highlights that research into comorbidities in PMR is, overall, methodologically inadequate and does not comprehensively cover all comorbidities. Future studies should consider a range of comorbidities in patients with a validated diagnosis of PMR in representative populations.
Keywords: Polymyalgia rheumatica, Giant cell arteritis, Systematic review, Comorbidities, Multimorbidity, Epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term glucocorticoid treatment in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica, giant cell arteritis, or both diseases: results from a national rheumatology database.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Apr;38(4):569-577. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3874-3. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29124397
-
The spectrum of conditions mimicking polymyalgia rheumatica in Northwestern Spain.J Rheumatol. 2000 Sep;27(9):2179-84. J Rheumatol. 2000. PMID: 10990231
-
Incidence and prevalence of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: A systematic literature review.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Oct;50(5):1040-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 32911281
-
COVID-19 outcomes in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica versus rheumatoid arthritis: A national, multicenter, cohort study.J Autoimmun. 2022 Oct;132:102868. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102868. Epub 2022 Jul 20. J Autoimmun. 2022. PMID: 35926375 Free PMC article.
-
Polymyalgia rheumatica: 125 years of epidemiological progress?Scott Med J. 2015 Feb;60(1):50-7. doi: 10.1177/0036933014551115. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Scott Med J. 2015. PMID: 25201886 Review.
Cited by
-
Norwegian society of rheumatology recommendations on diagnosis and treatment of patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica: a narrative review.BMC Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 4;8(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s41927-024-00422-6. BMC Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39490996 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic autoimmune disease as a cause of death: mortality burden and comorbidities.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Mar 2;60(3):1321-1330. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa537. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021. PMID: 32944773 Free PMC article.
-
Treat-to-target recommendations in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Jan 2;83(1):48-57. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223429. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 36828585 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot study of a nurse-led integrated care review (the INCLUDE review) for people with inflammatory rheumatological conditions in primary care: feasibility study findings.Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021 Jan 6;7(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40814-020-00750-7. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021. PMID: 33407943 Free PMC article.
-
The contributions of deleterious rare alleles in NLRP12 and inflammasome-related genes to polymyalgia rheumatica.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 4;14(1):490. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51320-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38177227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salvarani C, Macchioni PL, Tartoni PL, et al. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a 5-year epidemiologic and clinical study in Reggio Emilia, Italy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1987;5(3):205–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical