Osteogenic protein-1 attenuates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in a hyperosmotic culture
- PMID: 30459239
- PMCID: PMC6294645
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20181708
Osteogenic protein-1 attenuates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in a hyperosmotic culture
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Osteogenic protein-1 attenuates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in a hyperosmotic culture.Biosci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;44(8):BSR-2018-1708_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2018-1708_RET. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39171808 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have indicated that osteogenic protein-1 has protective effects on the biological functions of intervertebral disc cells. Hyperosmolarity is an important physicochemical factor within the disc nucleus pulposus (NP) region, which obviously promotes NP cell apoptosis.
Objective: To study the effects of osteogenic protein-1 (OP-1) on NP cell apoptosis induced by hyperosmolarity and the potential signaling transduction pathway.
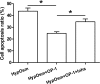
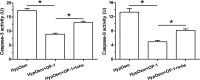
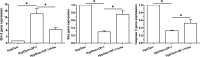
Methods: Rat NP cells were cultured in a hyperosmotic medium with or without OP-1 addition for 7 days. Inhibitor 294002 and inhibitor FK-506 were used to investigate the role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in this process. NP cell apoptosis were evaluated by cell apoptosis ratio, activity of caspase-3/9 and gene/protein expression of apoptosis-related molecules (Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-3/cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP).
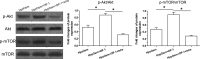
Results: OP-1 addition obviously decreased cell apoptosis ratio and caspase-3/9 activity, down-regulated gene/protein expression of pro-apoptosis molecules (Bax, caspase-3/cleaved casepase-3 and cleaved PARP), up-regulated gene/protein expression of anti-apoptosis molecule (Bcl-2) in a hyperosmotic culture. Moreover, OP-1 addition significantly increased protein expression of p-Akt and p-mTOR. Further analysis showed that addition of LY294002 and FK-506 partly attenuated these protective effects of OP-1 against NP cell apoptosis and activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in a hyperosmotic culture.
Conclusion: OP-1 can attenuate NP cell apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in a hyperosmotic culture. The present study sheds a new light on the protective role of OP-1 in regulating disc cell biology and provides some theoretical basis for the application of OP-1 in retarding/regenerating disc degeneration.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt/mTOR; cell apoptosis; intervertebral disc degeneration; nucleus pulposus; osteogenic protein-1.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
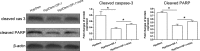
References
-
- Wang X., Wang B., Zou M., Li J., Lu G., Zhang Q.. et al. (2018) CircSEMA4B targets miR-431 modulating IL-1beta-induced degradative changes in nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral disc degeneration via Wnt pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1864, 3754–3768 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.08.033 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

