Targeting Metabolism, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes to Treat Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- PMID: 30459251
- PMCID: PMC6245219
- DOI: 10.2337/dbi18-0024
Targeting Metabolism, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes to Treat Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Abstract
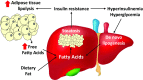
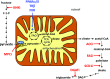
Obesity, insulin resistance, and diabetes are strongly linked to the accumulation of excessive lipids in the liver parenchyma, a condition known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Given its association with obesity and related metabolic diseases, it is not surprising that the prevalence of NAFLD has dramatically increased in the past few decades. NAFLD has become the most common liver disease in many areas of the world. The term, NAFLD, encompasses a spectrum of disorders that ranges from simple steatosis to steatosis with inflammatory lesions (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH]). Although simple steatosis might be relatively benign, epidemiologic studies have linked NASH to greatly increased risk of developing cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Yet despite this, there are no approved treatments for the disease, and it remains a significant unmet medical need. This Perspective will review some of the relevant literature on the topic and examine approved and experimental NASH therapeutic concepts that target intermediary metabolism, insulin resistance, and diabetes to treat this emerging public health problem.
© 2018 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Is insulin resistance the link?Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 1:55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25724480 Review.
-
Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021 Aug;17(8):484-495. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00507-z. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34131333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ectodysplasin A Is Increased in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, But Is Not Associated With Type 2 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 4;12:642432. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.642432. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33746906 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1261:223-229. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-7360-6_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33783745
-
Metabolic Spectrum of Liver Failure in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: From NAFLD to NASH to HCC.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 26;22(9):4495. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094495. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TM4SF5-mediated abnormal food-intake behavior and apelin expression facilitate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease features.iScience. 2023 Aug 14;26(9):107625. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107625. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37670786 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting hepatocyte carbohydrate transport to mimic fasting and calorie restriction.FEBS J. 2021 Jun;288(12):3784-3798. doi: 10.1111/febs.15482. Epub 2020 Jul 26. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 32654397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of sex and high-fat diet in metabolic and hypothalamic disturbances in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Sep 29;17(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01956-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32993686 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Autophagy in NASH and NASH-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 13;23(14):7734. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147734. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zaluzanin C Inhibits Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes into Mature Adipocytes.J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019 Jun;28(2):105-111. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2019.28.2.105. Epub 2019 Jun 30. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31294342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ekstedt M, Franzén LE, Mathiesen UL, et al. . Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology 2006;44:865–873 - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Blissett D, Blissett R, et al. . The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Hepatology 2016;64:1577–1586 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

