Oral Probiotics Ameliorate the Behavioral Deficits Induced by Chronic Mild Stress in Mice via the Gut Microbiota-Inflammation Axis
- PMID: 30459574
- PMCID: PMC6232506
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00266
Oral Probiotics Ameliorate the Behavioral Deficits Induced by Chronic Mild Stress in Mice via the Gut Microbiota-Inflammation Axis
Abstract
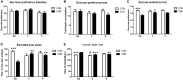
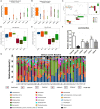
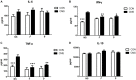
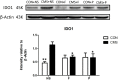
In recent years, a burgeoning body of research has revealed links between depression and the gut microbiota, leading to the therapeutic use of probiotics for stress-related disorders. In this study, we explored the potential antidepressant efficacy of a multi-strain probiotics treatment (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052, Lactobacillus plantarum R1012, and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in a chronic mild stress (CMS) mouse model of depression and determined its probable mechanism of action. Our findings revealed that mice subjected to CMS exhibited anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors in the sucrose preference test, elevated plus maze, and forced swim test, along with increased interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α, and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 levels in the hippocampus. Moreover, the microbiota distinctly changed from the non-stress group and was characterized by highly diverse bacterial communities associated with significant reductions in Lactobacillus species. Probiotics attenuated CMS-induced anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors, significantly increased Lactobacillus abundance, and reversed the CMS-induced immune changes in the hippocampus. Thus, the possible mechanism involved in the antidepressant-like activity of probiotics is correlated with Lactobacillus species via the gut microbiota-inflammation-brain axis.
Keywords: 3-dioxygenase; Bifidobacteria; Lactobacillus; chronic mild stress; indoleamine 2; inflammation; microbiota; probiotics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Administration of Lactobacillus helveticus NS8 improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused by chronic restraint stress.Neuroscience. 2015 Dec 3;310:561-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.033. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26408987
-
Exploring the Potential of Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175 as Promising Psychobiotics Using SHIME.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 21;15(6):1521. doi: 10.3390/nu15061521. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986251 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Administration of Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium Offers Enhanced Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activity in a Dose Dependent Manner.Brain Behav. 2025 May;15(5):e70564. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70564. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40384043 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of microbiota gut-brain axis in the manifestation of obsessive-compulsive disorder: Preclinical and clinical evidence.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 15;957:176014. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176014. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37619786 Review.
-
Immunology and probiotic impact of the newborn and young children intestinal microflora.Anaerobe. 2011 Dec;17(6):369-74. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Anaerobe. 2011. PMID: 21515397 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiome Analysis Reveals the Attenuation Effect of Lactobacillus From Yaks on Diarrhea via Modulation of Gut Microbiota.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 16;10:610781. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.610781. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33665171 Free PMC article.
-
Stressful events induce long-term gut microbiota dysbiosis and associated post-traumatic stress symptoms in healthcare workers fighting against COVID-19.J Affect Disord. 2022 Apr 15;303:187-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.02.024. Epub 2022 Feb 12. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 35157946 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of bacillus pumilus TS2 isolated from yaks on growth performance, gut microbial community, antioxidant activity, and cytokines related to immunity and inflammation in broilers.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Apr 26;11:1383262. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1383262. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38737458 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal Transplant and Bifidobacterium Treatments Modulate Gut Clostridium Bacteria and Rescue Social Impairment and Hippocampal BDNF Expression in a Rodent Model of Autism.Brain Sci. 2021 Aug 5;11(8):1038. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11081038. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34439657 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Supplementation and High-Intensity Interval Training Modify Anxiety-Like Behaviors and Corticosterone in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Mice.Nutrients. 2021 May 21;13(6):1762. doi: 10.3390/nu13061762. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34064242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burokas A., Arboleya S., Moloney R. D., Peterson V. L., Murphy K., Clarke G., et al. (2017). Targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis: prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice. Biol. Psychiatry 82 472–487. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.12.031 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

