Cerebral Venous Drainage in Patients With Space-Occupying Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction: Effects on Functional Outcome After Hemicraniectomy
- PMID: 30459703
- PMCID: PMC6232900
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00876
Cerebral Venous Drainage in Patients With Space-Occupying Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction: Effects on Functional Outcome After Hemicraniectomy
Abstract
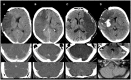
Background: Cerebral venous drainage might influence brain edema characteristics and functional outcome of patients with severe ischemic stroke. The purpose of the study was to evaluate whether hypoplasia of transverse sinuses or the internal jugular veins is associated with poor functional outcome in patients with space-occupying middle cerebral artery (MCA) infarction who underwent decompressive surgery. Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of patients with space-occupying MCA infarction treated with decompressive surgery at our university hospital. The transverse sinuses and the internal jugular veins were evaluated on baseline images and categorized as normal, hypoplastic or occluded. We defined composite variables for ipsilateral, contralateral or any abnormal cerebral venous drainage. We assessed the functional outcome at 12 months with the modified Rankin scale (mRS) score and defined poor functional outcome as mRS scores 5 and 6. Results: We analyzed 88 patients with available baseline imaging data [mean [SD] patient age 53 (±9) years; median[IQR] time to decompressive surgery 31(22-51) h]. At 12 months 44 patients (50%) had a poor outcome. In univariate analysis neither ipsilateral (OR 1.98;95%CI: 0.75-5.40), nor contralateral (OR 1.56;95%CI: 0.59-4.24) or any (OR 1.6; 95%CI: 0.68-3.79) hypoplasia or occlusion of venous drainage were significantly associated with poor functional outcome. In multivariate analyses, higher patient age (OR 1.07;95%CI 1.01-1.14) and baseline stroke severity (OR 3.42;95%CI 1.31-9.40) were independent predictors of poor functional outcome, but not ipsilateral hypoplasia or occlusion of venous drainage (OR 1.31;95%CI 0.47-3.67). Conclusions: The cerebral venous drainage pattern was not significantly associated with poor functional outcome in our cohort of patients with space-occupying MCA infarction who underwent decompressive surgery.
Keywords: cerebral sinus; cerebral veins; cerebral venous drainage; decompressive surgery; hemicraniectomy; middle cerebral artery infarction; space-occupying infarction; stroke.
Figures
References
-
- Hacke W, Schwab S, Horn M, Spranger M, De Georgia M, von Kummer R. ‘Malignant’ middle cerebral artery territory infarction: clinical course and prognostic signs. Arch Neurol. (1996) 53:309–15. - PubMed
-
- Frank JI. Large hemispheric infarction, deterioration, and intracranial pressure. Neurology (1995) 45:1286–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

