Future Perspectives on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and GLP-1/glucagon Receptor Co-agonists in the Treatment of NAFLD
- PMID: 30459715
- PMCID: PMC6232120
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00649
Future Perspectives on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and GLP-1/glucagon Receptor Co-agonists in the Treatment of NAFLD
Abstract
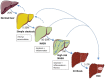
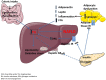
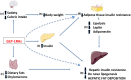
Along the obesity pandemic, the prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), often regarded as the hepatic manifestation of the metabolic syndrome, increases worldwide representing now the prevalent liver disease in western countries. No pharmacotherapy is approved for the treatment of NAFLD and, currently, the cornerstone treatment is lifestyle modifications focusing on bodyweight loss, notoriously difficult to obtain and even more difficult to maintain. Thus, novel therapeutic approaches are highly demanded. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. They exert their body weight-lowering effect by reducing satiety and food intake. GLP-1RAs have also been shown to reduce liver inflammation and fibrosis. Furthermore, glucagon receptor agonism is being investigated for the treatment of NAFLD due to its appetite and food intake-reducing effects, as well as its ability to increase lipid oxidation and thermogenesis. Recent studies suggest that glucagon receptor signaling is disrupted in NAFLD, indicating that supra-physiological glucagon receptor agonism might represent a new NAFLD treatment target. The present review provides (1) an overview in the pathophysiology of NAFLD, including the potential involvement of GLP-1 and glucagon, (2) an introduction to the currently available GLP-1RAs and (3) outlines the potential of emerging GLP-1RAs and GLP-1/glucagon receptor co-agonists in the treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: glucagon; glucagon-like peptide-1; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

