Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Host Cell Death Molecular Machinery
- PMID: 30459758
- PMCID: PMC6232773
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02379
Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Host Cell Death Molecular Machinery
Abstract
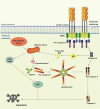
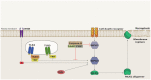
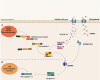
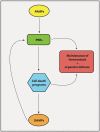
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) are proteins capable of recognizing molecules frequently found in pathogens (the so-called Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns-PAMPs), or molecules released by damaged cells (the Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns-DAMPs). They emerged phylogenetically prior to the appearance of the adaptive immunity and, therefore, are considered part of the innate immune system. Signals derived from the engagement of PRRs on the immune cells activate microbicidal and pro-inflammatory responses required to eliminate or, at least, to contain infectious agents. Molecularly controlled forms of cell death are also part of a very ancestral mechanism involved in key aspects of the physiology of multicellular organism, including the elimination of unwanted, damaged or infected cells. Interestingly, each form of cell death has its particular effect on inflammation and on the development of innate and adaptive immune responses. In this review article, we discuss some aspects of the molecular interplay between the cell death machinery and signals initiated by the activation of PRRs by PAMPs and DAMPs.
Keywords: PRR; apoptosis; inflammation; necroptosis; pathogen recognition receptor; pyroptosis.
Figures
References
-
- Janeway CA Jr. Pillars article: approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold spring harb symp quant biol. 1989. 54: 1–13. J Immunol. (2013) 191: 4475–4487. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway CA Jr. Innate immunity: impact on the adaptive immune response. Curr Opin Immunol. (1997) 9:4–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

