Sepsis and Nosocomial Infection: Patient Characteristics, Mechanisms, and Modulation
- PMID: 30459764
- PMCID: PMC6232897
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02446
Sepsis and Nosocomial Infection: Patient Characteristics, Mechanisms, and Modulation
Abstract
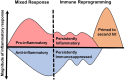
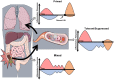
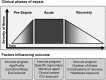
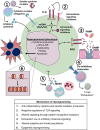
Sepsis is a leading cause of death worldwide. After initial trials modulating the hyperinflammatory phase of sepsis failed, generations of researchers have focused on evaluating hypo-inflammatory immune phenotypes. The main goal has been to develop prognostic biomarkers and therapies to reduce organ dysfunction, nosocomial infection, and death. The depressed host defense in sepsis has been characterized by broad cellular reprogramming including lymphocyte exhaustion, apoptosis, and depressed cytokine responses. Despite major advances in this field, our understanding of the dynamics of the septic host response and the balance of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cellular programs remains limited. This review aims to summarize the epidemiology of nosocomial infections and characteristic immune responses associated with sepsis, as well as immunostimulatory therapies currently under clinical investigation.
Keywords: SIRS; compensatory anti-inflammatory response; immunostimulation; immunosuppression; nosocomial infection; priming; sepsis.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham E, Wunderink R, Silverman H, Perl TM, Nasraway S, Levy H, et al. . Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor α in patients with sepsis syndrome. A randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial JAMA. J Am Med Assoc. (1995) 273:934–41. 10.1001/jama.273.12.934 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dhainaut JF, Tenaillon A, Le Tulzo Y, Schlemmer B, Solet JP, Wolff M, et al. . Platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist BN 52021 in the treatment of severe sepsis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial. BN 52021 Sepsis Study Group. Crit. Care Med. (1994) 22:1720–8. - PubMed
-
- Fisher CJ, Dhainaut JF, Opal SM, Pribble JP, Balk RA, Slotman GJ, et al. . Recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of patients with sepsis syndrome. Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phase III rhIL-1ra Sepsis Syndrome Study Group. JAMA (1994) 271:1836–43. 10.1001/jama.1994.03510470040032 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

