Predicting Diabetes Mellitus With Machine Learning Techniques
- PMID: 30459809
- PMCID: PMC6232260
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00515
Predicting Diabetes Mellitus With Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract
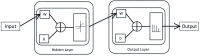
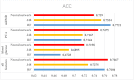
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by hyperglycemia. It may cause many complications. According to the growing morbidity in recent years, in 2040, the world's diabetic patients will reach 642 million, which means that one of the ten adults in the future is suffering from diabetes. There is no doubt that this alarming figure needs great attention. With the rapid development of machine learning, machine learning has been applied to many aspects of medical health. In this study, we used decision tree, random forest and neural network to predict diabetes mellitus. The dataset is the hospital physical examination data in Luzhou, China. It contains 14 attributes. In this study, five-fold cross validation was used to examine the models. In order to verity the universal applicability of the methods, we chose some methods that have the better performance to conduct independent test experiments. We randomly selected 68994 healthy people and diabetic patients' data, respectively as training set. Due to the data unbalance, we randomly extracted 5 times data. And the result is the average of these five experiments. In this study, we used principal component analysis (PCA) and minimum redundancy maximum relevance (mRMR) to reduce the dimensionality. The results showed that prediction with random forest could reach the highest accuracy (ACC = 0.8084) when all the attributes were used.
Keywords: decision tree; diabetes mellitus; feature ranking; machine learning; neural network; random forest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

