JAVELIN Head and Neck 100: a Phase III trial of avelumab and chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer
- PMID: 30461306
- PMCID: PMC11835014
- DOI: 10.2217/fon-2018-0405
JAVELIN Head and Neck 100: a Phase III trial of avelumab and chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer
Abstract
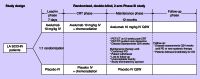
Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) is the standard of care for locoregionally advanced squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck (HNSCC). The immune checkpoint inhibitors nivolumab and pembrolizumab were recently approved by the US FDA for treatment of recurrent or metastatic HNSCC that are refractory to platinum chemotherapy. However, prospective studies incorporating immune checkpoint inhibitors in the definitive management of poor prognosis, nonmetastatic, locoregionally advanced HNSCC are lacking. The JAVELIN Head and Neck 100 study is a multinational, Phase III, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial assessing the efficacy of avelumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, in combination with CRT compared with placebo in combination with CRT for high-risk HNSCC. Trial registration: Javelin Head and Neck 100; NCT 02952586.
Keywords: PD-1; PD-L1; chemoradiotherapy; head and neck; immune checkpoint blockade; immunotherapy; locally advanced.
Conflict of interest statement
Y Yu has no relevant disclosures. NY Lee is an international principal investigator for the Javelin Head and Neck 100 study. She has also served as an advisor and consultant for Pfizer, Merck, Merck GMO, Sanofi Aventis and Lily. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit Ret al. . Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 136(5), e359–e386 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Grégoire V, Lefèbvre JL, Licitra Let al. . Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 21(Suppl. 5), 184–186 (2010). - PubMed
-
- O’Sullivan B, Huang SH, Su Jet al. . Development and validation of a staging system for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer by the International Collaboration on Oropharyngeal cancer Network for Staging (ICON-S): a multicentre cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 17(4), 440–451 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials