Interleukin-6 for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis with premature rupture of the membranes: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 30461611
- PMCID: PMC6392693
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013146
Interleukin-6 for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis with premature rupture of the membranes: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Premature rupture of the membranes (PROM) is the principal risk factor for neonatal sepsis. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been investigated for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis, but not for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis with PROM. The objective of this study is to investigate the early diagnostic value of IL-6 for neonatal sepsis with PROM.
Methods: The literature was searched using PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CNKI, Wan Fang, VIP, and CBM databases until March 2018. Each study was evaluated using Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies tool-2. We used a bivariate diagnostic random-effects model.
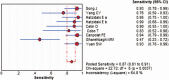
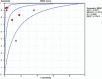
Results: The overall pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood rate, negative likelihood rate, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve were 0.85 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.81-0.91), 0.88 (95% CI: 0.86-0.91), 9.94 (95% CI: 4.27-23.15), 0.14 (95% CI: 0.06-0.32), 79.26 (95% CI: 23.42-268.26), and 0.9473, respectively, which showed high accuracy in diagnosing neonatal sepsis with PROM. The types of sepsis might be connected with the source of heterogeneity (P = .0351).
Conclusion: IL-6 is therefore a sensitive and specific diagnostic marker for the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis with PROM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A meta-analysis of interleukin-6 as a valid and accurate index in diagnosing early neonatal sepsis.Int Wound J. 2019 Apr;16(2):527-533. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13079. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Int Wound J. 2019. Retraction in: Int Wound J. 2025 Apr;22(4):e70633. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70633. PMID: 30734480 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Is neutrophil CD11b a special marker for the early diagnosis of sepsis in neonates? A systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2019 May 1;9(4):e025222. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025222. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31048432 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic value of interleukin 6 for neonatal sepsis: a Meta analysis].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Nov;17(11):1176-82. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26575874 Chinese.
-
The Value of Interleukin-10 in the Early Diagnosis of Neonatal Sepsis: A Meta-Analysis.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2021 Sep 1;22(9):e492-e501. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000002706. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33710072
-
Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil CD64 for neonatal sepsis.Ital J Pediatr. 2016 Jun 7;42(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13052-016-0268-1. Ital J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27268050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the cross-talk between mediators of infertility and COVID-19.Reprod Biol. 2021 Dec;21(4):100559. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2021.100559. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Reprod Biol. 2021. PMID: 34547545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of atosiban combined with ritodrine in the treatment of threatened preterm labor and related risk factors of different pregnancy outcomes.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Aug 15;14(8):5931-5940. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36105038 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin relieves the inflammation and pyroptosis of lipopolysaccharide-treated 1321N1 cells by regulating methyltransferase-like 3 -mediated NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 expression.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):6740-6749. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2045836. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35246004 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Intensive Care Unit Admission in COVID-19-Infected Pregnant Women Using Machine Learning.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 17;13(24):7705. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247705. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39768627 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogeny of plasma cytokine and chemokine concentrations across the first week of human life.Cytokine. 2021 Dec;148:155704. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155704. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 34597920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kayem G, Batteux F, Girard N, et al. Predictive value of vaginal IL-6 and TNF a bedside test repeated until delivery for the prediction of maternal-fetal infection in cases of premature rupture of membranes. Eur J Obst Gynecol Reprod Biol 2017;211:8–14. - PubMed
-
- Canpolat FE, Yiğit S, Korkmaz A, et al. Procalcitonin versus CRP as an early indicator of fetal infection in preterm premature rupture of membranes. Turk J Pediatr 2011;53:180–6. - PubMed
-
- Gulati S, Agrawal S, Raghunandan C, et al. Maternal serum interleukin-6 and its association with clinicopathological infectious morbidity in preterm premature rupture of membranes: a prospective cohort study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2011;25:1428–32. - PubMed
-
- Bigelow CA, Factor SH, Miller M, et al. Pilot randomized controlled trial to evaluate the impact of bed rest on maternal and fetal outcomes in women with preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Am J Perinatol 2016;33:356–63. - PubMed
-
- Pasquier JC, Picaud JC, Rabilloud M, et al. Neonatal outcomes after elective delivery management of preterm premature rupture of the membranes before 34 weeks’ gestation (DOMINOS study). Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2009;143:18–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

