Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma as a chest-wall mass: A case report
- PMID: 30461640
- PMCID: PMC6393079
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013291
Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma as a chest-wall mass: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the chest wall is extremely rare. A majority of the pleural lymphomas develop in patients with chronic tuberculous pyothorax. The underlying mechanism might be attributed to the sustained stimulation of chronic inflammation. Surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy can improve the outcome in some patients with lymphoma localized only in the chest wall. Thus, an early diagnosis of pyothorax-associated lymphoma is essential as it is a malignant, life-threatening condition.
Patient concerns: A 79-year-old male complained of left-side chest pain for more than 2 months, which was not alleviated with nitrates and aspirin. The patient presented an intermittent low fever, anorexia, and marasmus, accompanied by tuberculosis 40 years ago and chronic left-side pyothorax. Also, ANCA (antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody)-associated vasculitis occurred for >3years.
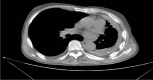
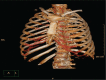
Diagnosis: Computed tomography scan showed a solid mass in the left lateral chest wall. The patient underwent ultrasonic-guided biopsy of the lesion. A diagnosis of primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the chest wall was established after histological examination.
Intervention: Due to advanced age and poor physical condition, the patient received CHOP chemotherapy at a reduced dose.
Outcomes: The patient died 5 days after the first cycle of chemotherapy with severe dyspnea and high fever.
Lessons: The chronic inflammation stimulation might result in the development of lymphoma in the chest wall of patients with long-term pyothorax, vasculitis, or other autoimmune diseases associated with malignancies. The fever, chest pain, or other nonspecific clinical symptoms in these patients should be under intensive focus as it might indicate the development of malignant lymphoma. Thus, histological examination in these patients is essential for accurate early diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma Complicated by Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis that was Successfully Treated with Rituximab-Containing Chemotherapy.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2015;55(1):39-43. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.55.39. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2015. PMID: 26106006
-
[A case of chronic tuberculous pyothorax associated malignant lymphoma].Kekkaku. 1996 Jun;71(6):415-21. Kekkaku. 1996. PMID: 8753018 Japanese.
-
Primary Malignant Lymphoma Originating from the Chest Wall without Preceding Pleural Disease.Intern Med. 2017;56(6):681-686. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7053. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28321070 Free PMC article.
-
[A case of T-cell malignant lymphoma developing in the chest wall of chronic pyothorax after artificial pneumothorax].Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 May;44(5):709-13. Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8965007 Review. Japanese.
-
Pancreatic T/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma: A case report and review of literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jun 28;23(24):4467-4472. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i24.4467. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28706431 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Presenting as a Primary Pleural Mass: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2022 Mar 2;14(3):e22765. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22765. eCollection 2022 Mar. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35371857 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Pleural Lymphoma in an Immune-Competent Patient: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge.J Pers Med. 2025 Apr 23;15(5):162. doi: 10.3390/jpm15050162. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 40423034 Free PMC article.
-
Pleural Marginal Zone Lymphoma Masquerading as Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Lung.Cureus. 2024 Nov 11;16(11):e73462. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73462. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39664121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luh SP, Wu RM, Kuo MS, et al. Pleural non-Hodgkin's lymphoma developing from long-standing pyothorax: report of a case. J Formos Med Assoc 1993;92:1111–3. - PubMed
-
- Ascani S, Piccioli M, Poggi S, et al. Pyothorax-associated lymphoma: description of the first two cases detected in Italy. Ann Oncol 1997;8:1133–8. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita T, Ishii K, Taira Y, et al. Malignant lymphoma arising from chronic tuberculous empyema. A case report. Acta Radiol 1997;38:833–5. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology& Genetics, Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2004.
-
- Molinie V, Pouchot J, Navratil E, et al. Primary Epstein-Barr virus–related non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the pleural cavity following long-standing tuberculous empyema. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1996;120:288–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

