Uncovering Bax inhibitor-1 dual role in the legume-rhizobia symbiosis in common bean roots
- PMID: 30462254
- PMCID: PMC6363093
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ery417
Uncovering Bax inhibitor-1 dual role in the legume-rhizobia symbiosis in common bean roots
Abstract
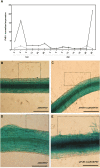
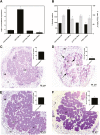
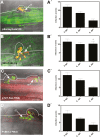
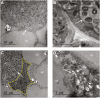
Bax-inhibitor 1 (BI-1) is a cell death suppressor conserved in all eukaryotes that modulates cell death in response to abiotic stress and pathogen attack in plants. However, little is known about its role in the establishment of symbiotic interactions. Here, we demonstrate the functional relevance of an Arabidopsis thaliana BI-1 homolog (PvBI-1a) to symbiosis between the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) and Rhizobium tropici. We show that the changes in expression of PvBI-1a observed during early symbiosis resemble those of some defence response-related proteins. By using gain- and loss-of-function approaches, we demonstrate that the overexpression of PvBI-1a in the roots of common bean increases the number of rhizobial infection events (and therefore the final number of nodules per root), but induces the premature death of nodule cells, affecting their nitrogen fixation efficiency. Nodule morphological alterations are known to be associated with changes in the expression of genes tied to defence, autophagy, and vesicular trafficking. Results obtained in the present work suggest that BI-1 has a dual role in the regulation of programmed cell death during symbiosis, extending our understanding of its critical function in the modulation of host immunity while responding to beneficial microbes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The non-specific phospholipase C of common bean PvNPC4 modulates roots and nodule development.PLoS One. 2025 May 5;20(5):e0306505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306505. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40323933 Free PMC article.
-
The Noncanonical Heat Shock Protein PvNod22 Is Essential for Infection Thread Progression During Rhizobial Endosymbiosis in Common Bean.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2019 Aug;32(8):939-948. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-19-0041-R. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2019. PMID: 30893001
-
Transcriptome analysis of the differential effect of the NADPH oxidase gene RbohB in Phaseolus vulgaris roots following Rhizobium tropici and Rhizophagus irregularis inoculation.BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 4;20(1):800. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6162-7. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31684871 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling in symbiotic root nodule formation.Essays Biochem. 1997;32:127-42. Essays Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9493016 Review.
-
How effectors promote beneficial interactions.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017 Aug;38:148-154. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2017.05.011. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28622658 Review.
Cited by
-
New methods for confocal imaging of infection threads in crop and model legumes.Plant Methods. 2021 Mar 7;17(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13007-021-00725-6. Plant Methods. 2021. PMID: 33678177 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Efficient Targeted Mutagenesis in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jul 11;13:935825. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.935825. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35898225 Free PMC article.
-
Symbiosis between cyanobacteria and plants: from molecular studies to agronomic applications.J Exp Bot. 2023 Oct 13;74(19):6145-6157. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad261. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 37422707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and lipidomic analyses suggest that Nostoc punctiforme, a plant-symbiotic cyanobacterium, does not produce sphingolipids.Access Microbiol. 2022 Jan 21;4(1):000306. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000306. eCollection 2022. Access Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35252750 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoprotective co-chaperone, AtBAG4, supports increased nodulation and seed protein content in chickpea without yield penalty.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 29;13(1):18553. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45771-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37899486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babaeizad V, Imani J, Kogel KH, Eichmann R, Hückelhoven R. 2008. Over-expression of theell death regulator BAX inhibitor-1 in barley confers reduced or enhanced susceptibility to distinct fungal pathogens. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 18, 455–463. - PubMed
-
- Bond JE, Gresshoff PM. 1993. Soybean transformation to study molecular physiology. In: Gresshoff, PM, ed. Plant responses to the environment. London: CRC Press, 25–44.
-
- Brechenmacher L, Kim MY, Benitez M, et al. . 2008. Transcription profiling of soybean nodulation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 21, 631–645. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Halane MK, Gassmann W, Stacey G. 2017. The role of plant innate immunity in the legume-rhizobium symbiosis. Annual Review of Plant Biology 68, 535–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

