MicroRNA-451a overexpression induces accelerated neuronal differentiation of Ntera2/D1 cells and ablation affects neurogenesis in microRNA-451a-/- mice
- PMID: 30462722
- PMCID: PMC6248975
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207575
MicroRNA-451a overexpression induces accelerated neuronal differentiation of Ntera2/D1 cells and ablation affects neurogenesis in microRNA-451a-/- mice
Abstract
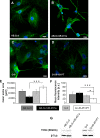
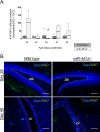
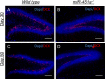
MiR-451a is best known for its role in erythropoiesis and for its tumour suppressor features. Here we show a role for miR-451a in neuronal differentiation through analysis of endogenous and ectopically expressed or silenced miR-451a in Ntera2/D1 cells during neuronal differentiation. Furthermore, we compared neuronal differentiation in the dentate gyrus of hippocampus of miR-451a-/- and wild type mice. MiR-451a overexpression in lentiviral transduced Ntera2/D1 cells was associated with a significant shifting of mRNA expression of the developmental markers Nestin, βIII Tubulin, NF200, DCX and MAP2 to earlier developmental time points, compared to control vector transduced cells. In line with this, accelerated neuronal network formation in AB.G.miR-451a transduced cells, as well as an increase in neurite outgrowth both in number and length was observed. MiR-451a targets genes MIF, AKT1, CAB39, YWHAZ, RAB14, TSC1, OSR1, POU3F2, TNS4, PSMB8, CXCL16, CDKN2D and IL6R were, moreover, either constantly downregulated or exhibited shifted expression profiles in AB.G.miR-451a transduced cells. Lentiviral knockdown of endogenous miR-451a expression in Ntera2/D1 cells resulted in decelerated differentiation. Endogenous miR-451a expression was upregulated during development in the hippocampus of wildtype mice. In situ hybridization revealed intensively stained single cells in the subgranular zone and the hilus of the dentate gyrus of wild type mice, while genetic ablation of miR-451a was observed to promote an imbalance between proliferation and neuronal differentiation in neurogenic brain regions, suggested by Ki67 and DCX staining. Taken together, these results provide strong support for a role of miR-451a in neuronal maturation processes in vitro and in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
miR-410 controls adult SVZ neurogenesis by targeting neurogenic genes.Stem Cell Res. 2016 Sep;17(2):238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 17. Stem Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27591480
-
Ras-GRF2 regulates nestin-positive stem cell density and onset of differentiation during adult neurogenesis in the mouse dentate gyrus.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017 Dec;85:127-147. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28966131
-
miR-451a Inhibition Reduces Established Endometriosis Lesions in Mice.Reprod Sci. 2019 Nov;26(11):1506-1511. doi: 10.1177/1933719119862050. Epub 2019 Jul 28. Reprod Sci. 2019. PMID: 31354069
-
[Overexpression of miR-451a inhibits cell proliferation by targeted macrophage migration inhibitory factor in HepG2 cells].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Dec;34(12):1091-1098. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30626475 Chinese.
-
miR-451a is underexpressed and targets AKT/mTOR pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 15;7(11):12731-47. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7262. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26871295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal expression of miR-let-7d-3p and miR-451a during gestation influences the neuropsychomotor development of 90 days old babies: "Pregnancy care, healthy baby" study.J Psychiatr Res. 2023 Feb;158:185-191. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.12.021. Epub 2022 Dec 29. J Psychiatr Res. 2023. PMID: 36587497 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time PCR Quantification of 87 miRNAs from Cerebrospinal Fluid: miRNA Dynamics and Association with Extracellular Vesicles after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 1;24(5):4751. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054751. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902179 Free PMC article.
-
Enriched Environment Induces Sex-Specific Changes in the Adult Neurogenesis, Cytokine and miRNA Expression in Rat Hippocampus.Biomedicines. 2023 May 2;11(5):1341. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051341. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239012 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Related sncRNAs in Human Hippocampal Tissue Samples: Focusing on Deregulated miRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 29;25(23):12872. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312872. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684581 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-451 in Inflammatory Diseases: Molecular Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Applications-A Comprehensive Review Beyond Oncology.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 16;47(2):127. doi: 10.3390/cimb47020127. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39996848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nan Y, Han L, Zhang A, Wang G, Jia Z, Yang Y, et al. MiRNA-451 plays a role as tumor suppressor in human glioma cells. Brain research. 2010;1359:14–21. Epub 2010/09/08. 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.074 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Du J, Liu S, He J, Liu X, Qu Y, Yan W, et al. MicroRNA-451 regulates stemness of side population cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(17):14993–5007. Epub 2015/04/29. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3802 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPmc4558131. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bitarte N, Bandres E, Boni V, Zarate R, Rodriguez J, Gonzalez-Huarriz M, et al. MicroRNA-451 is involved in the self-renewal, tumorigenicity, and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer stem cells. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio). 2011;29(11):1661–71. Epub 2011/09/29. 10.1002/stem.741 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gal H, Pandi G, Kanner AA, Ram Z, Lithwick-Yanai G, Amariglio N, et al. MIR-451 and Imatinib mesylate inhibit tumor growth of Glioblastoma stem cells. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2008;376(1):86–90. Epub 2008/09/04. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.107 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patz S, Trattnig C, Grunbacher G, Ebner B, Gully C, Novak A, et al. More than cell dust: microparticles isolated from cerebrospinal fluid of brain injured patients are messengers carrying mRNAs, miRNAs, and proteins. Journal of neurotrauma. 2013;30(14):1232–42. Epub 2013/01/31. 10.1089/neu.2012.2596 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

