Nanobody-Alkaline Phosphatase Fusion Protein-Based Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for One-Step Detection of Ochratoxin A in Rice
- PMID: 30463338
- PMCID: PMC6263964
- DOI: 10.3390/s18114044
Nanobody-Alkaline Phosphatase Fusion Protein-Based Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for One-Step Detection of Ochratoxin A in Rice
Abstract
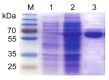
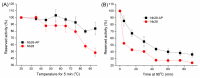
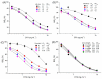
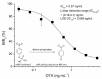
Ochratoxin A (OTA) has become one a focus of public concern because of its multiple toxic effects and widespread contamination. To monitor OTA in rice, a sensitive, selective, and one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using a nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein (Nb28-AP) was developed. The Nb28-AP was produced by auto-induction expression and retained an intact antigen-binding capacity and enzymatic activity. It exhibited high thermal stability and organic solvent tolerance. Under the optimal conditions, the developed assay for OTA could be finished in 20 min with a half maximal inhibitory concentration of 0.57 ng mL-1 and a limit of detection of 0.059 ng mL-1, which was 1.1 times and 2.7 times lower than that of the unfused Nb28-based ELISA. The Nb28-AP exhibited a low cross-reactivity (CR) with ochratoxin B (0.92%) and ochratoxin C (6.2%), and an ignorable CR (<0.10%) with other mycotoxins. The developed Nb-AP-based one-step ELISA was validated and compared with a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. The results show the reliability of Nb-AP-based one-step ELISA for the detection of OTA in rice.
Keywords: alkaline phosphatase; immunoassay; mycotoxin; nanobody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Some Naturally Occurring Substances: Food Items and Constituents, Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: IARC; Lyon, France: 1993.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

