Aberrant RNA Splicing in Cancer and Drug Resistance
- PMID: 30463359
- PMCID: PMC6266310
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10110458
Aberrant RNA Splicing in Cancer and Drug Resistance
Abstract
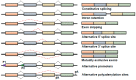
More than 95% of the 20,000 to 25,000 transcribed human genes undergo alternative RNA splicing, which increases the diversity of the proteome. Isoforms derived from the same gene can have distinct and, in some cases, opposing functions. Accumulating evidence suggests that aberrant RNA splicing is a common and driving event in cancer development and progression. Moreover, aberrant splicing events conferring drug/therapy resistance in cancer is far more common than previously envisioned. In this review, aberrant splicing events in cancer-associated genes, namely BCL2L1, FAS, HRAS, CD44, Cyclin D1, CASP2, TMPRSS2-ERG, FGFR2, VEGF, AR and KLF6, will be discussed. Also highlighted are the functional consequences of aberrant splice variants (BCR-Abl35INS, BIM-γ, IK6, p61 BRAF V600E, CD19-∆2, AR-V7 and PIK3CD-S) in promoting resistance to cancer targeted therapy or immunotherapy. To overcome drug resistance, we discuss opportunities for developing novel strategies to specifically target the aberrant splice variants or splicing machinery that generates the splice variants. Therapeutic approaches include the development of splice variant-specific siRNAs, splice switching antisense oligonucleotides, and small molecule inhibitors targeting splicing factors, splicing factor kinases or the aberrant oncogenic protein isoforms.
Keywords: alternative splicing; drug resistance; splice switching oligonucleotide; spliceosome; splicing factor; splicing factor inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Adams M.D., Kerlavage A.R., Fleischmann R.D., Fuldner R.A., Bult C.J., Lee N.H., Kirkness E.F., Weinstock K.G., Gocayne J.D., White O., et al. Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence. Nature. 1995;377:3–174. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

