Towards reducing the immunogenic potential of wheat flour: omega gliadins encoded by the D genome of hexaploid wheat may also harbor epitopes for the serious food allergy WDEIA
- PMID: 30463509
- PMCID: PMC6249860
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-018-1506-z
Towards reducing the immunogenic potential of wheat flour: omega gliadins encoded by the D genome of hexaploid wheat may also harbor epitopes for the serious food allergy WDEIA
Abstract
Background: Omega-5 gliadins are a group of highly repetitive gluten proteins in wheat flour encoded on the 1B chromosome of hexaploid wheat. These proteins are the major sensitizing allergens in a severe form of food allergy called wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (WDEIA). The elimination of omega-5 gliadins from wheat flour through biotechnology or breeding approaches could reduce the immunogenic potential and adverse health effects of the flour.
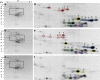
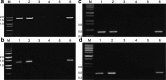
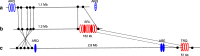
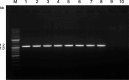
Results: A mutant line missing low-molecular weight glutenin subunits encoded at the Glu-B3 locus was selected previously from a doubled haploid population generated from two Korean wheat cultivars. Analysis of flour from the mutant line by 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis coupled with tandem mass spectrometry revealed that the omega-5 gliadins and several gamma gliadins encoded by the closely linked Gli-B1 locus were also missing as a result of a deletion of at least 5.8 Mb of chromosome 1B. Two-dimensional immunoblot analysis of flour proteins using sera from WDEIA patients showed reduced IgE reactivity in the mutant relative to the parental lines due to the absence of the major omega-5 gliadins. However, two minor proteins showed strong reactivity to patient sera in both the parental and the mutant lines and also reacted with a monoclonal antibody against omega-5 gliadin. Analysis of the two minor reactive proteins by mass spectrometry revealed that both proteins correspond to omega-5 gliadin genes encoded on chromosome 1D that were thought previously to be pseudogenes.
Conclusions: While breeding approaches can be used to reduce the levels of the highly immunogenic omega-5 gliadins in wheat flour, these approaches are complicated by the genetic linkage of different classes of gluten protein genes and the finding that omega-5 gliadins may be encoded on more than one chromosome. The work illustrates the importance of detailed knowledge about the genomic regions harboring the major gluten protein genes in individual wheat cultivars for future efforts aimed at reducing the immunogenic potential of wheat flour.
Keywords: Food allergy; Omega-5 gliadins; Proteomics; Reduced immunogenic potential; Wheat flour.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genetic differences in omega-gliadins involved in two different immediate food hypersensitivities to wheat.Allergy. 2007 Aug;62(8):890-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01456.x. Allergy. 2007. PMID: 17620066
-
Toward reducing the immunogenic potential of wheat flour: identification and characterization of wheat lines missing omega-5 gliadins encoded by the 1D chromosome.Theor Appl Genet. 2023 Mar 10;136(3):33. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04295-0. Theor Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 36897507
-
Assessment of the Allergenic Potential of Transgenic Wheat (Triticum aestivum) with Reduced Levels of ω5-Gliadins, the Major Sensitizing Allergen in Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Oct 28;63(42):9323-32. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03557. Epub 2015 Oct 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26447559
-
Molecular Diagnosis to IgE-mediated Wheat Allergy and Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 May 5;68(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09059-w. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40325270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis -importance of omega-5 gliadin and HMW-glutenin as causative antigens for wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis-.Allergol Int. 2009 Dec;58(4):493-8. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.09-RAI-0125. Epub 2009 Oct 25. Allergol Int. 2009. PMID: 19847096 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Trends in Proteomic Advances for Food Allergen Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2020 Aug 25;9(9):247. doi: 10.3390/biology9090247. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32854310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Getting in Shape: Updates in Exercise Anaphylaxis.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Nov;24(11):631-638. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01176-4. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 39294451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified acid-PAGE method for rapid screening and phenotyping of wheat gliadin mutant lines.MethodsX. 2020 Mar 20;7:100858. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2020.100858. eCollection 2020. MethodsX. 2020. PMID: 32322542 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and functional genomics analyses of gluten proteins and prospect for simultaneous improvement of end-use and health-related traits in wheat.Theor Appl Genet. 2020 May;133(5):1521-1539. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03557-5. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Theor Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 32020238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-Inflammatory Effect of Gliadins and Glutenins Extracted from Different Wheat Cultivars on an In Vitro 3D Intestinal Epithelium Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 26;22(1):172. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010172. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battais F, Courcoux P, Popineau Y, Kanny G, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Denery-Papini S. Food allergy to wheat: differences in immunoglobulin E-binding proteins as a function of age or symptoms. J Cereal Sci. 2005;42:109–117. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2005.01.004. - DOI
-
- Tye-Din JA, Stewart JA, Dromey JA, Beissbarth T, van Heel DA, Tatham A, Henderson K, Mannering SI, Gianfrani C, Jewell DP, Hill AVS, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J, Anderson RP. Comprehensive, quantitative mapping of T cell epitopes in gluten in celiac disease. Sci Transl Med. 2010;4(41):41ra51. - PubMed
-
- Altenbach Susan B., Kothari Kerry M. Omega gliadin genes expressed in Triticum aestivum cv. Butte 86: Effects of post-anthesis fertilizer on transcript accumulation during grain development. Journal of Cereal Science. 2007;46(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2007.02.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

