Aberrant expression of interleukin-23-regulated miRNAs in T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis
- PMID: 30463609
- PMCID: PMC6247500
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-018-1754-1
Aberrant expression of interleukin-23-regulated miRNAs in T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL)-23 can facilitate the differentiation of IL-17-producing helper T cells (Th17). The IL-23/IL-17 axis is known to play a key role in the immunopathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). We hypothesized that the expression of microRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) would be regulated by IL-23 and that these miRNAs could participate in the immunopathogenesis of AS.
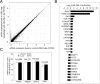
Methods: Expression profiles of human miRNAs in K562 cells, cultured in the presence or absence of IL-23 for 3 days, were analyzed by microarray. Potentially aberrantly expressed miRNAs were validated using T-cell samples from 24 patients with AS and 16 control subjects. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was conducted to search for gene expression and biological functions regulated by specific miRNAs in the IL-23-mediated signaling pathway.
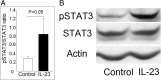
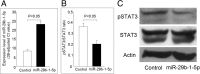
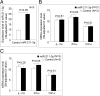
Results: Initial analysis revealed that the expression levels of 12 miRNAs were significantly higher, whereas those of 4 miRNAs were significantly lower, in K562 cells after coculture with IL-23 for 3 days. Among these IL-23-regulated miRNAs, the expression levels of miR-29b-1-5p, miR-4449, miR-211-3p, miR-1914-3p, and miR-7114-5p were found to be higher in AS T cells. The transfection of miR-29b-1-5p mimic suppressed IL-23-mediated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) phosphorylation in K562 cells. After NGS analysis and validation, we found that miR-29b-1-5p upregulated the expression of angiogenin, which was also upregulated in K562 cells after coculture with IL-23. Increased expression of miR-29b-1-5p or miR-211-3p could enhance interferon-γ expression.
Conclusions: Among the miRNAs regulated by IL-23, expression levels of five miRNAs were increased in T cells from patients with AS. The transfection of miR-29b-1-5p mimic could inhibit the IL-23-mediated STAT3 phosphorylation and might play a role in negative feedback control in the immunopathogenesis of AS.
Keywords: Angiogenin; Ankylosing spondylitis; IL-23; MicroRNAs; STAT3; T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional review board of Buddhist Dalin Tzu Chi Hospital, Taiwan (no. B10502002). Signed informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Australo-Anglo-American Spondylitis Consortium (TASC) Burton PR, Clayton DG, Cardon LR, Craddock N, et al. Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1329–1337. doi: 10.1038/ng.2007.17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

