Novel Roles for SUMOylation in Cellular Plasticity
- PMID: 30463679
- PMCID: PMC6456908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.10.001
Novel Roles for SUMOylation in Cellular Plasticity
Abstract
Cell fate transitions involve rapid changes in gene expression patterns, yet the role of post-translational modifications in these processes remains underexplored. A recent study identifies SUMOylation as a guardian of cell identity that acts during differentiation and reprogramming by reinforcing active enhancers and maintaining silenced heterochromatin in a context-specific manner.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
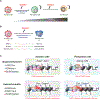
Comment on
-
SUMO Safeguards Somatic and Pluripotent Cell Identities by Enforcing Distinct Chromatin States.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Nov 1;23(5):742-757.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30401455
References
-
- Deribe YL et al. (2010) Post-translational modifications in signal integration. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17 (6), 666–72. - PubMed
-
- Flotho A and Melchior F (2013) Sumoylation: a regulatory protein modification in health and disease. Annu Rev Biochem 82, 357–85. - PubMed
-
- Cossec J et al. (2018) SUMO safeguards somatic and pluripotent cell identities by enforcing distinct chromatin states. Cell Stem Cell. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

