Infarct-Sparing Effect of Adenosine A2B Receptor Agonist Is Primarily Due to Its Action on Splenic Leukocytes Via a PI3K/Akt/IL-10 Pathway
- PMID: 30463755
- PMCID: PMC6251504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.06.042
Infarct-Sparing Effect of Adenosine A2B Receptor Agonist Is Primarily Due to Its Action on Splenic Leukocytes Via a PI3K/Akt/IL-10 Pathway
Abstract
Background: Adenosine A2B receptor (A2BAR) agonist reduces myocardial reperfusion injury by acting on inflammatory cells. Recently, a cardiosplenic axis was shown to mediate the myocardial postischemic reperfusion injury. This study aimed to explore whether the infarct-squaring effect of A2BAR agonist was primarily due to its action on splenic leukocytes.
Methods: C57BL6 (wild type [WT]) mice underwent 40 min of left coronary artery occlusion followed by 60 min of reperfusion. A2BAR knockout (KO) and interleukin (IL)-10KO mice served as donors for splenic leukocytes. Acute splenectomy was performed 30 min before ischemia. The acute splenic leukocyte adoptive transfer was performed by injecting 5 × 106 live splenic leukocytes into splenectomized mice. BAY 60-6583, an A2BAR agonist, was injected by i.v. 15 min before ischemia. The infarct size (IS) was determined using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride and Phthalo blue staining. The expression of p-Akt and IL-10 was estimated by Western blotting. Immunofluorescence staining assessed the localization of IL-10 expression.
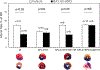
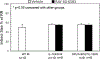
Results: BAY 60-6583 reduced the myocardial IS in intact mice but failed to reduce the same in splenectomized mice, which had a smaller IS than intact mice. BAY 60-6583 reduced the IS in splenectomized mice with the acute transfer of WT splenic leukocytes; however, it did not protect the heart of splenectomized mice with the acute transfer of A2BRKO splenic leukocytes. Furthermore, BAY 60-6583 increased the levels of p-Akt and IL-10 in the WT spleen. Moreover, it did not exert any protective effect in IL-10KO mice.
Conclusions: A2BAR activation before ischemia stimulated the IL-10 production in splenic leukocytes via a PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory effects that limited the myocardial reperfusion injury.
Keywords: Adenosine A2B receptor; Myocardial reperfusion injury; PI3K/Akt; Splenic leukocytes.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Adenosine 2B Receptor Activation Reduces Myocardial Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Anti-Inflammatory Macrophages Differentiation via PI3K/Akt Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:585297. doi: 10.1155/2015/585297. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26161239 Free PMC article.
-
Splenic leukocytes mediate the hyperglycemic exacerbation of myocardial infarct size in mice.Basic Res Cardiol. 2015;110(4):39. doi: 10.1007/s00395-015-0496-3. Epub 2015 May 27. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26014921
-
The spleen contributes importantly to myocardial infarct exacerbation during post-ischemic reperfusion in mice via signaling between cardiac HMGB1 and splenic RAGE.Basic Res Cardiol. 2016 Nov;111(6):62. doi: 10.1007/s00395-016-0583-0. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Basic Res Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27645145 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of the Beta2 Adrenergic Receptor at Reperfusion Limits Myocardial Reperfusion Injury via an Interleukin-10-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Pathway in the Spleen.Circ J. 2018 Oct 25;82(11):2829-2836. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-18-0061. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Circ J. 2018. PMID: 30158399 Free PMC article.
-
The resurgence of A2B adenosine receptor signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 May;1808(5):1329-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.05.016. Epub 2010 May 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20546702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A2B Adenosine Receptor and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 17;20(20):5139. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205139. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31627281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Nucleoside Agonists of the Adenosine Receptors: An Overview.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Oct 8;12(4):150. doi: 10.3390/ph12040150. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31597388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosterism vs. Orthosterism: Recent Findings and Future Perspectives on A2B AR Physio-Pathological Implications.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 24;12:652121. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.652121. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33841166 Free PMC article.
-
A2B adenosine receptor signaling and regulation.Purinergic Signal. 2025 Apr;21(2):201-220. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-10025-y. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Purinergic Signal. 2025. PMID: 38833181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAFA4-IL-10 axis potentiate immunotherapy for airway allergy by induction of specific regulatory T cells.NPJ Vaccines. 2022 Oct 31;7(1):133. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00559-w. NPJ Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 36316414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takano H, Bolli R, Black RG Jr, Kodani E, Tang XL, et al. A(1) or A(3) adenosine receptors induce late preconditioning against infarction in conscious rabbits by different mechanisms. Circulation research 2001:88:520–528. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Cerniway RJ, Byford AM, Berr SS, French BA, et al. Cardiac overexpression of A1-adenosine receptor protects intact mice against myocardial infarction. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2002:282:H949–955. - PubMed
-
- Nayeem MA, Matherne GP, Mustafa SJ Ischemic and pharmacological preconditioning induces further delayed protection in transgenic mouse cardiac myocytes over-expressing adenosine A1 receptors (A1AR): role of A1AR, iNOS and K(ATP) channels. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s archives of pharmacology 2003:367:219–226. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Day YJ, Toufektsian MC, Xu Y, Ramos SI, et al. Myocardial infarct-sparing effect of adenosine A2A receptor activation is due to its action on CD4+ T lymphocytes. Circulation 2006:114:2056–2064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

