An investigational RNAi therapeutic targeting Factor XII (ALN-F12) for the treatment of hereditary angioedema
- PMID: 30463937
- PMCID: PMC6348991
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.068916.118
An investigational RNAi therapeutic targeting Factor XII (ALN-F12) for the treatment of hereditary angioedema
Abstract
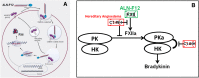
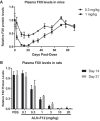
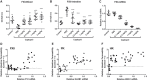
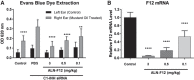
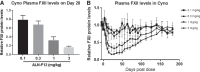
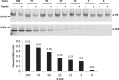
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a genetic disorder mostly caused by mutations in the C1 esterase inhibitor gene (C1INH) that results in poor control of contact pathway activation and excess bradykinin generation. Bradykinin increases vascular permeability and is ultimately responsible for the episodes of swelling characteristic of HAE. We hypothesized that the use of RNA interference (RNAi) to reduce plasma Factor XII (FXII), which initiates the contact pathway signaling cascade, would reduce contact pathway activation and prevent excessive bradykinin generation. A subcutaneously administered GalNAc-conjugated small-interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting F12 mRNA (ALN-F12) was developed, and potency was evaluated in mice, rats, and cynomolgus monkeys. The effect of FXII reduction by ALN-F12 administration was evaluated in two different vascular leakage mouse models. An ex vivo assay was developed to evaluate the correlation between human plasma FXII levels and high-molecular weight kininogen (HK) cleavage. A single subcutaneous dose of ALN-F12 led to potent, dose-dependent reduction of plasma FXII in mice, rats, and NHP. In cynomolgus monkeys, a single subcutaneous dose of ALN-F12 at 3 mg/kg resulted in >85% reduction of plasma FXII. Administration of ALN-F12 resulted in dose-dependent reduction of vascular permeability in two different mouse models of bradykinin-driven vascular leakage, demonstrating that RNAi-mediated reduction of FXII can potentially mitigate excess bradykinin stimulation. Lastly, ex vivo human plasma HK cleavage assay indicated FXII-dependent bradykinin generation. Together, these data suggest that RNAi-mediated knockdown of FXII by ALN-F12 is a potentially promising approach for the prophylactic treatment of HAE.
Keywords: Factor XII; GalNAc-siRNA; HK cleavage; bradykinin; hereditary angioedema; vascular permeability.
© 2019 Liu et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of liver-derived factor XII by GalNAc-siRNA ALN-F12 prevents thrombosis in mice without impacting hemostatic function.Thromb Res. 2020 Dec;196:200-205. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.08.040. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Thromb Res. 2020. PMID: 32896690
-
Plasmin is a natural trigger for bradykinin production in patients with hereditary angioedema with factor XII mutations.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Nov;138(5):1414-1423.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.02.021. Epub 2016 Apr 6. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27130860
-
A mechanism for hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor: an inhibitory regulatory role for the factor XII heavy chain.Blood. 2019 Mar 7;133(10):1152-1163. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-06-860270. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30591525 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary and acquired C1-inhibitor-dependent angioedema: from pathophysiology to treatment.Ann Med. 2016;48(4):256-67. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2016.1162909. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Ann Med. 2016. PMID: 27018196 Review.
-
Biochemistry, molecular genetics, and clinical aspects of hereditary angioedema with and without C1 inhibitor deficiency.Allergol Int. 2023 Jul;72(3):375-384. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2023.04.004. Epub 2023 May 9. Allergol Int. 2023. PMID: 37169642 Review.
Cited by
-
Next generation anticoagulants: a spotlight on the potential role of activated factors XII and XI.Expert Rev Hematol. 2023 Jul-Dec;16(10):711-714. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2023.2245973. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Expert Rev Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37542390 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The FXII c.-4T>C Polymorphism as a Disease Modifier in Patients With Hereditary Angioedema Due to the FXII p.Thr328Lys Variant.Front Genet. 2020 Sep 10;11:1033. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.01033. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33133137 Free PMC article.
-
Lanadelumab Injection Treatment For The Prevention Of Hereditary Angioedema (HAE): Design, Development And Place In Therapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Oct 22;13:3635-3646. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S192475. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31695331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of Oligonucleotides to the Liver with GalNAc: From Research to Registered Therapeutic Drug.Mol Ther. 2020 Aug 5;28(8):1759-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.06.015. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32592692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical manifestations of hereditary angioedema and a systematic review of treatment options.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021 Apr 3;6(3):394-403. doi: 10.1002/lio2.555. eCollection 2021 Jun. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34195359 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
