Function, clinical application, and strategies of Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer
- PMID: 30464224
- PMCID: PMC6748147
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-018-0231-3
Function, clinical application, and strategies of Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer
Abstract
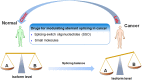
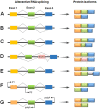
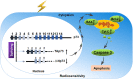
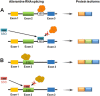
Pre-mRNA splicing is a fundamental process that plays a considerable role in generating protein diversity. Pre-mRNA splicing is also the key to the pathology of numerous diseases, especially cancers. In this review, we discuss how aberrant splicing isoforms precisely regulate three basic functional aspects in cancer: proliferation, metastasis and apoptosis. Importantly, clinical function of aberrant splicing isoforms is also discussed, in particular concerning drug resistance and radiosensitivity. Furthermore, this review discusses emerging strategies how to modulate pathologic aberrant splicing isoforms, which are attractive, novel therapeutic agents in cancer. Last we outline current and future directions of isoforms diagnostic methodologies reported so far in cancer. Thus, it is highlighting significance of aberrant splicing isoforms as markers for cancer and as targets for cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Mural RJ, Sutton GG, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–51. - PubMed
-
- Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1413–5. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe BJ. The relationship between alternative splicing and proteomic complexity. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42:407–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

