Mycophenolate therapy in interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features: a cohort study
- PMID: 30464490
- PMCID: PMC6219314
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S173154
Mycophenolate therapy in interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features: a cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: International experts recently characterized interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF) as a provisional diagnosis for patients with interstitial lung disease who have characteristics of autoimmune disease but do not meet criteria for a specific autoimmune disease. We describe clinical characteristics of IPAF patients and examine responses to mycophenolate as a therapy for IPAF.
Methods: This retrospective cohort included adult patients meeting European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society classification criteria for IPAF. Sociodemographic, clinical, and pulmonary function test data were abstracted for patients with and without mycophenolate treatment and followed longitudinally from interstitial lung disease diagnosis for change in pulmonary function test results.
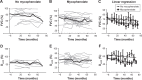
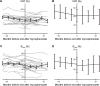
Results: We identified 52 patients who met criteria for IPAF. Of 52 IPAF patients, 24 did not receive mycophenolate and 28 did, with median time to mycophenolate treatment 22 months. Changes in FVC% and percentage predicted lung diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO%) between the mycophenolate-treated and untreated groups were not significantly different (FVC% change P=0.08, DLCO% change P=0.17). However, there was a trend toward more rapid baseline decline of both FVC% and DLCO% in the mycophenolate-treated cohort before vs after mycophenolate therapy. The slope of both FVC% and DLCO% values improved after onset of mycophenolate exposure for the treated group, although this finding was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Patients with IPAF might benefit from mycophenolate therapy. Larger prospective clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy of mycophenolate for patients who meet criteria for IPAF.
Keywords: autoimmune disease; connective tissue disease; interstitial lung disease; mycophenolate.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Fischer A, Antoniou KM, Brown KK, et al. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society research statement: interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Eur Respir J. 2015;46(4):976–987. - PubMed
-
- Swigris JJ, Olson AL, Fischer A, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil is safe, well tolerated, and preserves lung function in patients with connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease. Chest. 2006;130(1):30–36. - PubMed
-
- Goh NS, Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S, et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a simple staging system. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177(11):1248–1254. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

