SIRT6 overexpression induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibiting NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 30464510
- PMCID: PMC6219112
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S179866
SIRT6 overexpression induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibiting NF-κB signaling
Retraction in
-
SIRT6 Overexpression Induces Apoptosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling [Retraction].Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Feb 24;17:161-162. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S465407. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38426082 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Previous reports show that SIRT6 serves as a critical modulator of the development of multiple malignancies as well as other disorders. However, its role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is unknown. Thus, we elucidated the effects of SIRT6 on the survival of NPC cells, and modulation of cell death.
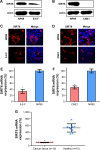
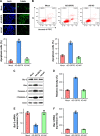
Methods: We found that expression of SIRT6 is downregulated in ten human NPC specimens as well as in the human NPC cell lines, 5-8 F and CNE1, as compared with that in healthy tissues and normal nasopharyngeal NP69 cells. The MTT assay and colony formation assay revealed that upregulation of SIRT6 impaired the proliferation, as well as the survival of 5-8 F and CNE1 cells. The TUNEL assay, annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide, and flow cytometry were performed to detect apoptosis. The results revealed that the expression of SIRT6 resulted in increased apoptosis.
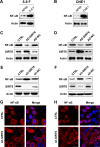
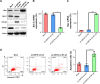
Results: Western blotting results showed that SIRT6 overexpression decreased anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 levels, whereas it promoted an increase in pro-apoptotic Bax and cleaved caspase-3 levels. Moreover, NF-κB levels were markedly reduced in cells expressing SIRT6, whereas they were increased in cells transfected with shRNA-SIRT6. Recovery of NF-κB expression was found to counter the suppressive influence of SIRT6 on NPC cell survival, whereas, NF-κB knockdown increased apoptosis of NPC cells.
Conclusion: Thus, the findings of our study offer insight into the biological and molecular mechanisms underlying the development of NPC and may lead to the development of new and innovative strategies for the treatment of NPC.
Keywords: NF-κB; SIRT6; apoptosis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simvastatin induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through NF-κB signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jun;24(12):6726-6734. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202006_21660. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32633363
-
PinX1-Promoted Autophagy Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting the NF-κB/p65 Signaling Pathway in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Aug 17;28(8):170. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2808170. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37664923
-
URG4-silencing suppresses cell proliferation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through induction of apoptosis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Mar;22(6):1717-1725. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201803_14585. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29630117
-
MicroRNA-19b-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting TNFAIP3/NF-κB axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 5;35(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0465-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27919278 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of ribophorin II is required for viability of nasopharyngeal cancer cells by regulating JAK1/STAT3 activation.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021 Aug;43(4):471-477. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2021.1942038. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021. PMID: 34184962
Cited by
-
The Two-Faced Role of SIRT6 in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 8;13(5):1156. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051156. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Sirtuin 6 in the Deacetylation of Histone Proteins as a Factor in the Progression of Neoplastic Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):497. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010497. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT6 Widely Regulates Aging, Immunity, and Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 6;12:861334. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.861334. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35463332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NAD metabolism in aging and cancer.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Nov;245(17):1594-1614. doi: 10.1177/1535370220929287. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32500741 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT6 inhibits metastasis by suppressing SNAIL expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2021 Jan 1;14(1):63-74. eCollection 2021. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33532024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wei WI, Sham JS. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2005;365(9476):2041–2054. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Fee WE, Ng WT, Chan LK. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: salvage of local recurrence. Oral Oncol. 2012;48(9):768–774. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Ding W, Chen C, Niu Z, Pan M, Zhang H. Meta-analysis of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in the treatment of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015;11(Suppl 2):C191–C195. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

