Low expression level of ASK1-interacting protein-1 correlated with tumor angiogenesis and poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer
- PMID: 30464518
- PMCID: PMC6219119
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S178131
Low expression level of ASK1-interacting protein-1 correlated with tumor angiogenesis and poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the expression of tumor suppressor protein ASK1-interacting protein-1 (AIP1) in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and its role in tumor progression, angiogenesis, and prognosis.
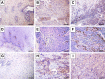
Methods: A total of 117 biopsy samples were obtained from ESCC patients. None of the patients had distant metastasis before surgery, and did not receive preoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of AIP1 protein and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) in ESCC specimens collected from 117 patients who underwent esophageal cancer radical surgery. Microvessel density (MVD) was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining of vascular endothelial CD34. The correlation between AIP1 protein and clinicopathological characteristics, tumor angiogenesis, and prognosis was analyzed.
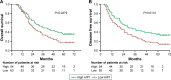
Results: The downregulation of AIP1 protein in esophageal carcinoma tissues was detected in 63 cases. This downregulation significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis, clinicopathological staging, and tumor MVD (P<0.05). Survival analysis showed that ESCC patients with a low expression of AIP1, a high expression of VEGFR2, and a high level of MVD had a lower 5-year survival rate (P<0.05). Multivariate analysis confirmed that the downregulation of AIP1 significantly affected patient survival.
Conclusion: The downregulation of AIP1 correlated with ESCC progression, tumor angiogenesis, and poor prognosis. AIP1 could be a promising biomarker for predicting ESCC prognosis and a potential target for anti-angiogenic therapy.
Keywords: ASK1-interacting protein-1; angiogenesis; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; microvessel density.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low Expression of ASK1-Interacting Protein-1 Is Significantly Correlated with Tumor Angiogenesis and Poor Survival in Patients with Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 10;12:10739-10747. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S222332. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31849482 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of microvessel density in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma-a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Nov;227:153644. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153644. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 34634564
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors (Flt-1 and Flk-1) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2002 Nov-Dec;22(6C):3977-84. Anticancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12553021
-
Metastasis-associated protein 1 nuclear expression is closely associated with tumor progression and angiogenesis in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer.World J Surg. 2012 Mar;36(3):623-31. doi: 10.1007/s00268-011-1421-z. World J Surg. 2012. PMID: 22270988
-
Expression of PC cell-derived growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their clinicopathologic significance.Chin Med J (Engl). 2008 May 20;121(10):881-6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008. PMID: 18706200
Cited by
-
Cancer Angiogenesis and Opportunity of Influence on Tumor by Changing Vascularization.J Pers Med. 2022 Feb 22;12(3):327. doi: 10.3390/jpm12030327. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35330327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Up-regulation of SOCS4 promotes cell proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 May;10(5):2416-2427. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-700. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116557 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Impact of the Angiogenic Gene POSTN and Its Related Genes on Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 27;12:699824. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.699824. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35832544 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic model based on oxidative stress-related genes in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): predicting patient outcomes and therapy responses.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):3152-3174. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-888. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39669999 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Carnitine/Organic Cation Transporter Novel 2 in the Clinical Outcome of Patients With Locally Advanced Esophageal Carcinoma Treated With Oxaliplatin.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 16;12:684545. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.684545. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34603016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang M, Smith JS, Wei WQ. Tissue protein biomarker candidates to predict progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 - PubMed
-
- Ren Y, Cao B, Law S, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes cancer cell migration and angiogenic factors expression: a prognostic marker of human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(17):6190–6197. - PubMed
-
- Mariette C, Balon JM, Piessen G, Fabre S, van Seuningen I, Triboulet JP. Pattern of recurrence following complete resection of esophageal carcinoma and factors predictive of recurrent disease. Cancer. 2003;97(7):1616–1623. - PubMed
-
- Okawa T, Naomoto Y, Nobuhisa T, et al. Heparanase is involved in angiogenesis in esophageal cancer through induction of cyclooxygenase-2. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(22):7995–8005. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

