OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG positive expression correlates with poor differentiation, advanced disease stages, and worse overall survival in HER2+ breast cancer patients
- PMID: 30464534
- PMCID: PMC6228048
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S173522
OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG positive expression correlates with poor differentiation, advanced disease stages, and worse overall survival in HER2+ breast cancer patients
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the correlations of expression of OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG with clinicopathological features and overall survival (OS) in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer (BC) patients.
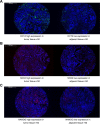
Methods: One hundred and thirty-four surgical HER2+ BC patients who received doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel and trastuzumab adjuvant therapy were enrolled in this study. Immunofluorescence assay was used to detect OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG expressions. The median follow-up duration was 104 months, and the last follow-up date was December 31, 2017.
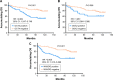
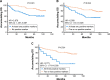
Results: The expressions of OCT4 (P=0.001), SOX2 (P=0.003), and NANOG (P=0.005) were higher in tumor tissues compared with paired adjacent tissues. OCT4 positive expression was associated with poor pathological differentiation (P=0.028), larger tumor size (P=0.022), advanced N stage (P<0.001), and higher TNM stage (P<0.001). SOX2 positive expression was correlated with poor pathological differentiation (P=0.005), larger tumor size (P=0.013), and increased T stage (P=0.024). NANOG positive expression was associated with poor pathological differentiation (P=0.028), higher N stage (P=0.001), and elevated TNM stage (P=0.001). Kaplan-Meier curves disclosed that OCT4 (P=0.001) and NANOG (P=0.001) positive expressions were associated with worse OS, while SOX2 (P=0.058) positive expression was only numerically correlated with poor OS, but without statistical significance. Further analyses revealed that co-expression of these three biomarkers disclosed even better predictive value for shorter OS.
Conclusion: OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG positive expressions correlate with poor differentiation and advanced disease stage, and OCT4 and NANOG present with predictive values for poor OS in HER2+ BC patients.
Keywords: biomarker; clinicopathological features; predictive value; prognosis; tumor tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Haghighat S, Akbari ME, Ghaffari S, Yavari P. Standardized breast cancer mortality rate compared to the general female population of Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(11):5525–5528. - PubMed
-
- Carlomagno C, Perrone F, Gallo C, et al. c-erb B2 overexpression decreases the benefit of adjuvant tamoxifen in early-stage breast cancer without axillary lymph node metastases. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(10):2702–2708. - PubMed
-
- Pritchard KI, Shepherd LE, O’Malley FP, et al. HER2 and responsiveness of breast cancer to adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(20):2103–2111. - PubMed
-
- Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(31):3997–4013. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

