Cost-consequence model comparing eltrombopag versus romiplostim for adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 30464563
- PMCID: PMC6219311
- DOI: 10.2147/CEOR.S177324
Cost-consequence model comparing eltrombopag versus romiplostim for adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia
Abstract
Background: Thrombopoietin-receptor agonists eltrombopag (EPAG) and romiplostim (ROMI) are treatment options for adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (cITP) who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids or immunoglobulins.
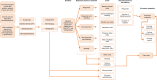
Methods: A cost-consequence model was developed to evaluate the costs relative to treatment success of EPAG, ROMI, and watch and rescue (W&R) in previously treated patients. The primary endpoint assessed was severe bleeding, derived from all identified phase III registered clinical trials. Health outcomes were compared via indirect treatment comparison. Costs incorporated in the model included drug and administration, routine care, rescue medications, bleeding-related adverse events, other adverse events, and mortality costs. A trial (26-week) time horizon was used, as certain endpoints used in the model were bound to within-trial results.
Results: In the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, the overall estimated cost per patient for EPAG was US$66,560 compared to US$91,039 for ROMI and US$30,099 for W&R. Compared to the ITT population, the difference in cost between EPAG and ROMI was slightly greater in splenectomized patients (US$65,998 for EPAG compared to US$91,485 for ROMI) and slightly less in non-splenectomized patients (US$67,151 for EPAG compared to US$91,455 for ROMI), though the overall trend remained the same. When assessing cost per severe bleeding event avoided in the ITT population, EPAG dominated (less expensive, more effective) ROMI. Sensitivity analyses confirmed these results.
Conclusion: EPAG was preferred over ROMI in the treatment of cITP, largely driven by the reduction in severe bleeding events associated with its use.
Keywords: USA; chronic immune thrombocytopenia; cost analysis; cost consequence; eltrombopag; romiplostim.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure M Bhor, Q Said, and B Elliott are employees of Novartis Pharmaceuticals. A Briggs received personal fees from Novartis for this study. He also received personal fees from Amgen, Bayer, Eisai, BMS, Astra Zeneca and Merck for activities ourside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Segal JB, Powe NR. Prevalence of immune thrombocytopenia: analyses of administrative data. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(11):2377–2383. - PubMed
-
- Terrell DR, Beebe LA, Vesely SK, Neas BR, Segal JB, George JN. The incidence of immune thrombocytopenic purpura in children and adults: A critical review of published reports. Am J Hematol. 2010;85(3):174–180. - PubMed
-
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute [Accessed September 26, 2018];Immune Thrombocytopenia. 2012 Available from: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/immune-thrombocytopenia.
-
- Cheng G, Saleh MN, Marcher C, et al. Eltrombopag for management of chronic immune thrombocytopenia (RAISE): a 6-month, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2011;377(9763):393–402. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources