Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation
- PMID: 30464573
- PMCID: PMC6217131
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S140188
Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation
Abstract
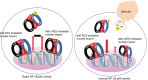
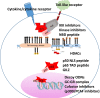
The transcription factor NF-κB is a critical regulator of immune and inflammatory responses. In mammals, the NF-κB/Rel family comprises five members: p50, p52, p65 (Rel-A), c-Rel, and Rel-B proteins, which form homo- or heterodimers and remain as an inactive complex with the inhibitory molecules called IκB proteins in resting cells. Two distinct NF-κB signaling pathways have been described: 1) the canonical pathway primarily activated by pathogens and inflammatory mediators, and 2) the noncanonical pathway mostly activated by developmental cues. The most abundant form of NF-κB activated by pathologic stimuli via the canonical pathway is the p65:p50 heterodimer. Disproportionate increase in activated p65 and subsequent transactivation of effector molecules is integral to the pathogenesis of many chronic diseases such as the rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, and even neurodegenerative pathologies. Hence, the NF-κB p65 signaling pathway has been a pivotal point for intense drug discovery and development. This review begins with an overview of p65-mediated signaling followed by discussion of strategies that directly target NF-κB p65 in the context of chronic inflammation.
Keywords: NF-κB; inflammation; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM. The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(1):17–26. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

