Celecoxib in breast cancer prevention and therapy
- PMID: 30464589
- PMCID: PMC6208493
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S178567
Celecoxib in breast cancer prevention and therapy
Abstract
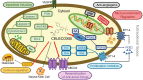
Breast cancer has a high incidence worldwide. The results of substantial studis reveal that inflammation plays an important role in the initiation, development, and aggressiveness of many malignancies. The use of celecoxib, a novel NSAID, is repetitively associated with the reduced risk of the occurrence and progression of a number of types of cancer, particularly breast cancer. This observation is also substantiated by various meta-analyses. Clinical trials have been implemented on integration treatment of celecoxib and shown encouraging results. Celecoxib could be treated as a potential candidate for antitumor agent. There are, nonetheless, some unaddressed questions concerning the precise mechanism underlying the anticancer effect of celecoxib as well as its activity against different types of cancer. In this review, we discuss different mechanisms of anticancer effect of celecoxib as well as preclinical/clinical results signifying this beneficial effect.
Keywords: COX-2; breast cancer; celecoxib; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials