Downregulation of FOXO6 in breast cancer promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and facilitates migration and proliferation of cancer cells
- PMID: 30464613
- PMCID: PMC6215919
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S157661
Downregulation of FOXO6 in breast cancer promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and facilitates migration and proliferation of cancer cells
Abstract
Purpose: Increasing evidence indicates that members of forkhead transcription factor family (FOXO) play key roles in cell proliferation and apoptosis in multiple cancers, including prostate cancer. However, the underlying mechanism of FOXO6 was not yet known. The aim of our work is to investigate the function of FOXO6 in breast cancer.
Methods: In the present study, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting analyses were used to detect the expression of FOXO6 in breast cancer tissues and cell lines.
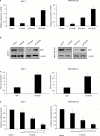
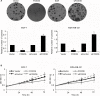
Results: The results revealed that FOXO6 was downregulated in breast cancer tissues and cell lines, compared with adjacent normal tissues and MCF-10A cells, respectively. Moreover, the expression of FOXO6 was associated with the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) indicator proteins, such as E-cadherin and N-cadherin. Additionally, our findings suggested that FOXO6 expression was negatively associated with tumor size (p=0.002), pathological grade (p=0.018) and lymph node metastasis (p=0.003). Sirt6 has been found to promote cell proliferation and metastasis in several cancers, and quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays indicated FOXO6 transcriptionally regulated Sirt6 expression. Furthermore, various functional experiments, including wound healing assay, transwell invasion assay, colony formation assay and Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, revealed that FOXO6 suppressed cell migration, invasion, and proliferation of breast cancer cells.
Conclusion: In conclusion, FOXO6 serves as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer, and suppresses EMT through regulation of Sirt6.
Keywords: EMT; FOXO6; Sirt6; breast cancer; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Liu H, Yin J, Wang H, et al. FOXO3a modulates WNT/β-catenin signaling and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2015;27(3):510–518. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

