Time-dependent behaviour of bone accentuates loosening in the fixation of fractures using bone-screw systems
- PMID: 30464838
- PMCID: PMC6215240
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.710.BJR-2018-0085.R1
Time-dependent behaviour of bone accentuates loosening in the fixation of fractures using bone-screw systems
Abstract
Aims: Loosening is a well-known complication in the fixation of fractures using devices such as locking plates or unilateral fixators. It is believed that high strains in the bone at the bone-screw interface can initiate loosening, which can result in infection, and further loosening. Here, we present a new theory of loosening of implants. The time-dependent response of bone subjected to loads results in interfacial deformations in the bone which accumulate with cyclical loading and thus accentuates loosening.
Methods: We used an 'ideal' bone-screw system, in which the screw is subjected to cyclical lateral loads and trabecular bone is modelled as non-linear viscoelastic and non-linear viscoelastic-viscoplastic material, based on recent experiments, which we conducted.
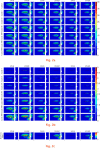
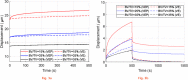
Results: We found that the interfacial deformation in the bone increases with the number of cycles, and the use of a non-linear viscoelastic-viscoplastic model results in larger deformations, some of which are irrecoverable. There is an apparent trend in which interfacial deformations increase with increasing porosity of bone.
Conclusion: The developed time-dependent model of the mechanical behaviour of bone permits prediction of loosening due to cyclical loads, which has not been possible previously. Application of this model shows that implant loosening will be accentuated by cyclical loading due to physiological activities, and the risks of loosening are greater in osteoporotic patients.Cite this article: S. Xie, K. Manda, P. Pankaj. Time-dependent behaviour of bone accentuates loosening in the fixation of fractures using bone-screw systems. Bone Joint Res 2018;7:580-586. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.710.BJR-2018-0085.R1.
Keywords: Bone volume ratio; Cyclic loading; Irrecoverable strain; Viscoelastic-viscoplastic.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement: None declared
Figures


References
-
- MacLeod A, Pankaj P. Computer Simulation of Fracture Fixation Using Extramedullary Devices: An Appraisal. In: Doyle B, Miller K, Wittek A, Nielsen PMF, eds. Computational Biomechanics for Medicine: Fundamental Science and Patient-specific Applications. New York: Springer, 2014:87–99.
-
- Taylor M, Tanner KE. Fatigue failure of cancellous bone: a possible cause of implant migration and loosening. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1997;79-B:181–182. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi RL, Borgersen SE. Nonlinear finite element contact analysis of dental implant components. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1993;8:655–661. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson FE, Pankaj P, Simpson AHRW. Bone properties affect loosening of half-pin external fixators at the pin-bone interface. Injury 2012;43:1764–1770. - PubMed
-
- Huiskes R, Chao EYS, Crippen TE. Parametric analyses of pin-bone stresses in external fracture fixation devices. J Orthop Res 1985;3:341–349. - PubMed

