Potential of ramucirumab in treating hepatocellular carcinoma patients with elevated baseline alpha-fetoprotein
- PMID: 30464931
- PMCID: PMC6219272
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S157413
Potential of ramucirumab in treating hepatocellular carcinoma patients with elevated baseline alpha-fetoprotein
Abstract
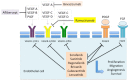
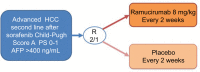
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents ~90% of primary liver cancers and constitutes a major global health problem. Since a decade ago, the management of advanced disease that cannot be locally treated has mainly been based on multi-targeted antiangiogenic therapies. Some have demonstrated improvement in overall survival over best supportive care in first- and second-line treatment. This study focused on the efficacy of antiangiogenics in patients with advanced HCC and particularly the rising role of ramucirumab in patients with elevated alpha-fetoprotein at diagnosis.
Keywords: antiangiogenic drugs; hepatocellular carcinoma; ramucirumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379(9822):1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Sangiovanni A, Prati GM, Fasani P, et al. The natural history of compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus: a 17-year cohort study of 214 patients. Hepatology. 2006;43(6):1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35(3):519–524. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

