Natalizumab may control immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced limbic encephalitis
- PMID: 30465016
- PMCID: PMC6225924
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000439
Natalizumab may control immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced limbic encephalitis
Figures
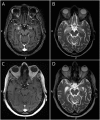
References
-
- Williams TJ, Benavides DR, Patrice KA, et al. . Association of autoimmune encephalitis with combined immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment for metastatic cancer. JAMA Neurol 2016;73:928–933. - PubMed
-
- Hottinger AF. Neurologic complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Curr Opin Neurol 2016;29:806–812. - PubMed
-
- Cuzzubbo S, Javeri F, Tissier M, et al. . Neurological adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: review of the literature. Eur J Cancer 2017;73:1–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
