Fungal Diseases in the 21st Century: The Near and Far Horizons
- PMID: 30465032
- PMCID: PMC6241320
- DOI: 10.20411/pai.v3i2.249
Fungal Diseases in the 21st Century: The Near and Far Horizons
Abstract
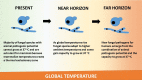
Fungal diseases became a major medical problem in the second half of the 20th century when advances in modern medicine together with the HIV epidemic resulted in large numbers of individuals with impaired immunity. Fungal diseases are difficult to manage because they tend to be chronic, hard to diagnose, and difficult to eradicate with antifungal drugs. This essay considers the future of medical mycology in the 21st century, extrapolating from current trends. In the near horizon, the prevalence of fungal diseases is likely to increase, as there will be more hosts with impaired immunity and drug resistance will inevitably increase after selection by antifungal drug use. We can expect progress in the development of new drugs, diagnostics, vaccines, and immunotherapies. In the far horizon, humanity may face new fungal diseases in association with climate change. Some current associations between chronic diseases and fungal infections could lead to the establishment of fungi as causative agents, which will greatly enhance their medical importance. All trends suggest that the importance of fungal diseases will increase in the 21st century, and enhanced human preparedness for this scourge will require more research investment in this group of infectious diseases.
Keywords: Fungal Diseases; diagnostics; drug resistance; global warming; immunotherapies; mycology.
Figures
References
-
- Currie BP, Casadevall A. Estimation of the prevalence of Cryptococcus neoformans infection in New York City in 1991. The First National Conference on Human Retroviruses and Related Infections. 1993; Washington, D.C.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
