Measuring medical students' reflection on their learning: modification and validation of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ)
- PMID: 30466427
- PMCID: PMC6251170
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-018-1384-y
Measuring medical students' reflection on their learning: modification and validation of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ)
Abstract
Background: Reflection on learning is an essential component of effective learning. Deconstructing the components of reflection on learning using a self-regulated learning (SRL) framework, allows the assessment of students' ability to reflect on their learning. The aim of this study was to validate an instrument to measure medical students' reflection on their learning.
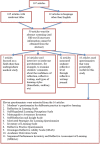
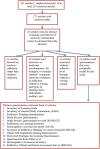
Methods: A systematic search was conducted to identify the most suitable instrument to measure students' reflection on their learning based on the theoretical framework of SRL. The search identified the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) which contained five subscales: internal goal orientation, self-efficacy, critical thinking, metacognitive/self-regulation, help seeking and peer learning. Using the original MSLQ as the foundation, we carried out three phases of a research program to develop a useful set of items: an expert panel's review of items, a substantial pilot study, and a factor analysis of ratings of a modified set of items by preclinical and final year medical students.
Results: The factor analysis of the Modified MSLQ extracted four subscales with reasonable internal consistency: self-orientation, critical thinking, self-regulation and feedback-seeking. Each subscale correlates highly with the Modified MSLQ score, with modest inter-correlations between the subscales suggesting that they are measuring different components of the total score.
Conclusion: Medical students and their educators need to be able to monitor their learning in their complex academic and clinical environments. The Modified MSLQ provides a means of investigating and tracking individual medical students' reflections on their learning.
Keywords: Instrument; MSLQ; Medical students; Reflection on learning.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Diantha Soemantri, MD, MMedEd, PhD (DS) is a senior lecturer in medical education at the Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia. Her main research interest is on students learning and assessment, specifically related to feedback and reflection.
Geoff Mccoll, BMedSc, MBBS, MEd, PhD (GM) is currently the Executive Dean, Faculty of Medicine University of Queensland. Previously he was the Head of the Melbourne Medical School and Professor of Medical Education and Training at the University of Melbourne. He is currently the Chair of the Australian Medical Council’s Medical School Assessment Committee.
Agnes Dodds, BA (hons), M.A. (AD) is an Associate Professor in the Department of Medical Education in the Melbourne Medical School. Her research interests are in evaluation and young adult development, particularly of high achieving students in professional courses.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study has been approved by the University of Melbourne Human Research Ethics Committee. All participants provided their consent to participate in this study by completing and handing in the questionnaires. Information on the voluntary nature of their participation and confidentiality of the data was provided beforehand.
Consent for publication
The consent provided by the study participants includes the permission to use the data for presentation and publication of the study.
Competing interests
The authors report no competing financial and non-financial interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Using multiple self-regulated learning measures to understand medical students' biomedical science learning.Med Educ. 2020 Aug;54(8):727-737. doi: 10.1111/medu.14079. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 32012330
-
Assessing student engagement and self-regulated learning in a medical gross anatomy course.Anat Sci Educ. 2015 Mar-Apr;8(2):104-10. doi: 10.1002/ase.1463. Epub 2014 May 20. Anat Sci Educ. 2015. PMID: 24845421
-
The Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire: score validity among medicine residents.Med Educ. 2011 Dec;45(12):1230-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2011.04077.x. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Med Educ. 2011. PMID: 22026751
-
Development of a Web-based question database for students' self-assessment.Acad Med. 2002 Sep;77(9):925. Acad Med. 2002. PMID: 12228094 Review.
-
Beyond Grades: Harnessing Self-Regulated Learning to Empower Underperforming Students.Niger Med J. 2025 Apr 3;66(1):26-35. doi: 10.71480/nmj.v66i1.689. eCollection 2025 Jan-Feb. Niger Med J. 2025. PMID: 40309551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding Student Characteristics in the Development of Active Learning Strategies.Med Sci Educ. 2022 Apr 30;32(3):615-626. doi: 10.1007/s40670-022-01550-9. eCollection 2022 Jun. Med Sci Educ. 2022. PMID: 35818614 Free PMC article.
-
Surveying Undergraduate Medical Students' Motivational Orientations and Learning Strategies in the First and Last Year of Medical School.Med Sci Educ. 2024 May 29;34(4):783-793. doi: 10.1007/s40670-024-02067-z. eCollection 2024 Aug. Med Sci Educ. 2024. PMID: 39099868 Free PMC article.
-
Correlates, motivating factors, and barriers of engaging in regular self-reflection among public health students in higher education-A mixed methods approach.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 3;10:1023439. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1023439. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36408036 Free PMC article.
-
Telling My Story: Applying Storytelling to Complex Economic Data.East Econ J. 2023;49(3):328-348. doi: 10.1057/s41302-023-00242-5. Epub 2023 Mar 16. East Econ J. 2023. PMID: 37274304 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire among clinical clerkship students in Malaysia.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 8;20(4):e0319763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319763. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40198634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott J. Learning makes sense: re-creating education for a changing future. Letchworth: Education. 2000;1994.
-
- Ertmer Peggy A., Newby Timothy J. The expert learner: Strategic, self-regulated, and reflective. Instructional Science. 1996;24(1):1–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00156001. - DOI
-
- Zimmerman BJ. Models of self-regulated learning and academic achievement. In: Zimmerman BJ, Schunk DH, editors. Self-regulated learning and academic achievement: theory, research, and practice. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1989. pp. 1–26.
-
- Thompson S, Thompson N. The critically reflective practitioner. 1. New York: Palgrave Macmillan; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous