Safety and Efficacy of Biodegradable Polymer-biolimus-eluting Stents (BP-BES) Compared with Durable Polymer-everolimus-eluting Stents (DP-EES) in Patients Undergoing Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- PMID: 30468035
- PMCID: PMC6331317
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2018.0097
Safety and Efficacy of Biodegradable Polymer-biolimus-eluting Stents (BP-BES) Compared with Durable Polymer-everolimus-eluting Stents (DP-EES) in Patients Undergoing Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Abstract
Background and objectives: There are no data comparing clinical outcomes of complex percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) between biodegradable polymer-biolimus-eluting stents (BP-BES) and durable polymer-everolimus-eluting stents (DP-EES). We sought to evaluate the safety and efficacy of BP-BES compared with DP-EES in patients undergoing complex PCI.
Methods: Patients enrolled in the SMART-DESK registry were stratified into 2 categories based on the complexity of PCI. Complex PCI was defined as having at least one of the following features: unprotected left main lesion, ≥2 lesions treated, total stent length >40 mm, minimal stent diameter ≤2.5 mm, or bifurcation as target lesion. The primary outcome was target lesion failure (TLF), defined as a composite of cardiac death, target vessel-related myocardial infarction (TV-MI), or target lesion revascularization (TLR) at 2 years of follow-up.
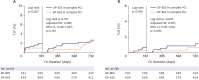
Results: Of 1,999 patients, 1,145 (57.3%) underwent complex PCI: 521 patients were treated with BP-BES and 624 with DP-EES. In propensity-score matching analysis (481 pairs), the risks of TLF (3.8% vs. 5.2%, adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.578; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.246-1.359; p=0.209), cardiac death (2.5% vs. 2.5%, adjusted HR, 0.787; 95% CI, 0.244-2.539; p=0.689), TV-MI (0.5% vs. 0.4%, adjusted HR, 1.128; 95% CI, 0.157-8.093; p=0.905), and TLR (1.1% vs. 2.9%, adjusted HR, 0.390; 95% CI, 0.139-1.095; p=0.074) did not differ between 2 stent groups after complex PCI.
Conclusions: Clinical outcomes of BP-BES were comparable to those of DP-EES at 2 years after complex PCI. Our data suggest that use of BP-BES is acceptable, even for complex PCI.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Drug-eluting stents; Percutaneous coronary intervention.
Copyright © 2019. The Korean Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Park DW, Park SW. Stent thrombosis in the era of the drug-eluting stent. Korean Circ J. 2005;35:791–794.
-
- Minha S, Barbash IM, Dvir D, et al. Second-generation everolimus-eluting stents compared to first-generation drug-eluting stents in patients treated for multivessel disease. J Interv Cardiol. 2013;26:561–569. - PubMed
-
- Grundeken MJ, Wykrzykowska JJ, Ishibashi Y, et al. First generation versus second generation drug-eluting stents for the treatment of bifurcations: 5-year follow-up of the LEADERS all-comers randomized trial. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;87:E248–60. - PubMed
-
- Vlachojannis GJ, Smits PC, Hofma SH, et al. Biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease: final 5-year report from the COMPARE II trial (abluminal biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent) JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10:1215–1221. - PubMed
-
- Im E, Kim GS, Shin DH, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of a biodegradable polymer-based biolimus-eluting stent. J Interv Cardiol. 2016;29:162–167. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

